Key Takeaways:
- The global semiconductor market is booming, projected to reach $1 trillion by 2030.
- Bangladesh’s strategic location near major markets and shipping routes offers advantages for developing its semiconductor industry.
- Major challenges include a lack of skilled workforce, high initial investment costs, inadequate infrastructure, and strong competition from established players.
- Success in the semiconductor industry could help diversify Bangladesh’s economy and reduce dependence on the ready-made garment sector.
The global semiconductor industry is a cornerstone of modern technology, powering everything from smartphones to cars. While growing rapidly, Bangladesh’s role in this market remains small. To expand, the country must overcome several challenges, including developing a skilled workforce, securing investment, and improving infrastructure. Addressing these issues can position Bangladesh as a key player in the global semiconductor market, bringing substantial economic benefits.
You can also read: US, China, and Europe: Economic Race of Century
Local demand for electronics is rising, which can drive industry expansion. Bangladesh also boasts a large, young workforce, providing a demographic advantage. With proper support and strategic investments, the country can increase its presence in the global semiconductor market by leveraging its growing consumer base and strategic location.
The Global Semiconductor Market
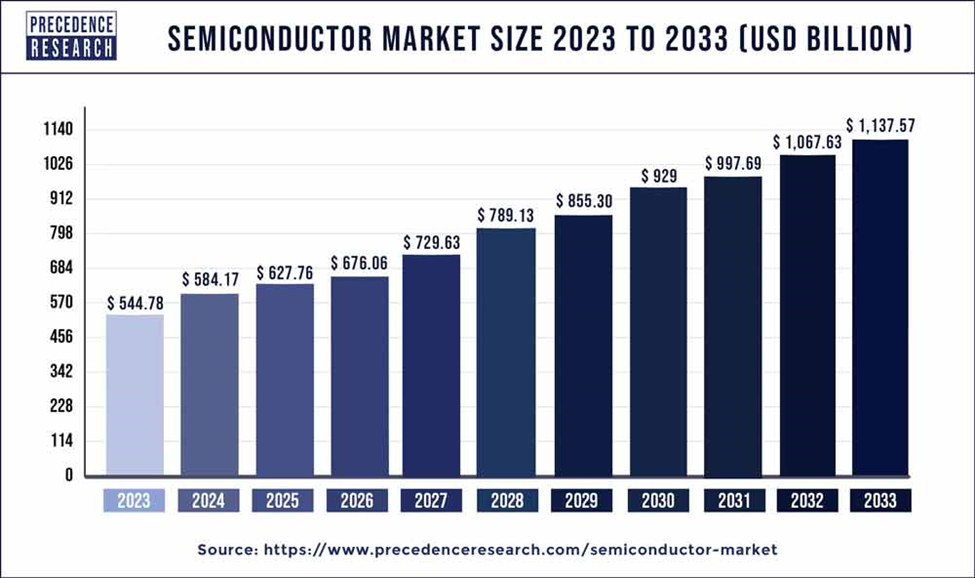
The global semiconductor market is thriving, with projections indicating it will reach $1 trillion by 2030 {figure 1}. These tiny electronic components are essential for devices like phones and computers. Although Bangladesh’s semiconductor industry currently generates only about $5 million annually, there’s room for growth.
Strategic and Military Importance
Semiconductors hold strategic importance for several reasons. They’re vital for modern technology, enabling advancements in artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and telecommunications. Countries investing in semiconductors can reduce dependence on imports, enhancing national security and economic stability.
These components are embedded in countless devices, from smartphones and computers to automobiles and household appliances. They’re crucial in medical devices, aiding in diagnostics and patient care, and in communication infrastructure, facilitating data transmission across networks and the internet.
In the military sphere, semiconductors are indispensable. They power advanced communication systems, ensuring secure and reliable information exchange. In weapons systems, they enable precision targeting and control, improving effectiveness and reducing collateral damage. Military vehicles, including drones and fighter jets, rely on semiconductors for navigation, surveillance, and operational efficiency.
Semiconductors also play a vital role in cybersecurity, protecting sensitive data and infrastructure from threats. They support the development of AI and machine learning in military applications, providing strategic advantages in intelligence and decision-making.
US Investment in Semiconductor Industries
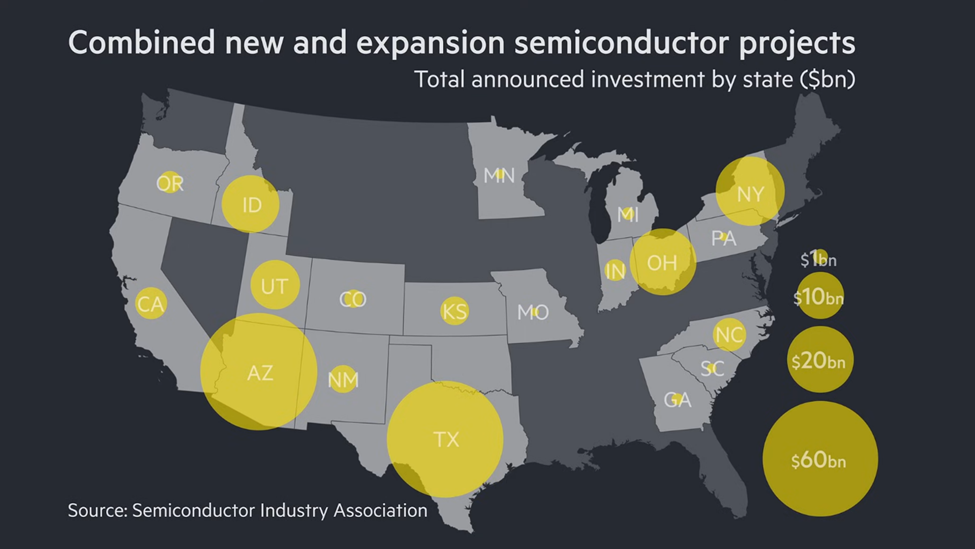
The United States has made significant strides in expanding its semiconductor industry to maintain technological leadership and national security. In 2022, the CHIPS and Science Act allocated $52 billion to boost domestic semiconductor manufacturing and research. This investment aims to reduce dependency on foreign chip supplies, which are critical for various industries, including defense and technology.
Major companies like Intel, Micron, and TSMC have announced substantial investments in new U.S. manufacturing facilities. These investments are expected to create thousands of high-tech jobs and enhance the resilience of the U.S. semiconductor supply chain. The focus on R&D aims to drive innovation in AI, 5G, and other emerging technologies, ensuring the U.S. remains at the forefront of global technological advancements.
Bangladesh’s Strategic Location
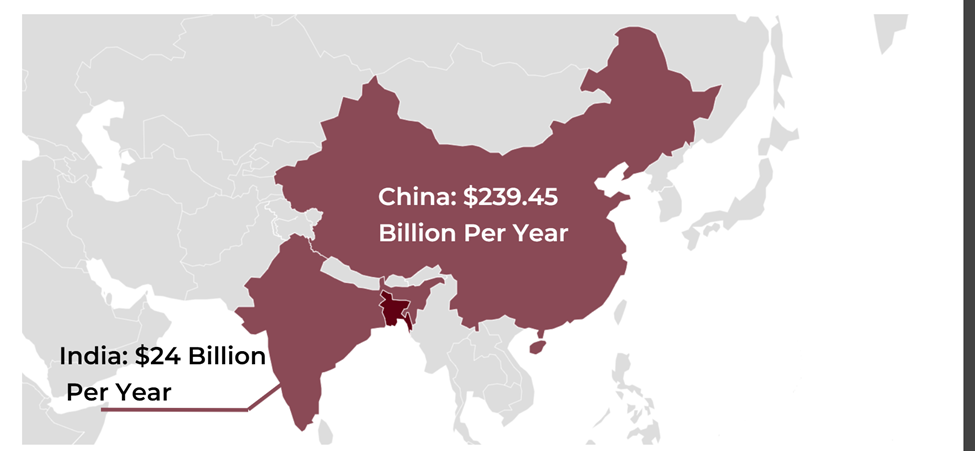
Bangladesh’s location in South Asia offers a key advantage. Its proximity to major markets like India and China can attract investment in semiconductor manufacturing. Bangladesh can serve growing regional demands, reducing reliance on distant suppliers. The country’s position near major shipping routes facilitates efficient import of raw materials and export of finished products, potentially lowering transport costs and improving supply chain logistics.
This strategic location also presents opportunities for regional collaboration and integration into the global semiconductor value chain. With the right investments, Bangladesh can leverage its geographic position to become a significant player in the industry.
Primary Challenges
Bangladesh faces several hurdles in developing its semiconductor industry.
- The lack of a skilled workforce is a major issue, with a shortage of trained engineers and technicians hampering the growth of local manufacturers.
- High initial investment requirements for setting up semiconductor fabs deter many potential investors.
- Infrastructure is another significant barrier.
- Efficient transport and logistics are essential for the industry, and Bangladesh must improve its ports, airports, and roads to facilitate the import of raw materials and export of finished products.
- Market entry is challenging due to competition from established players like China, India, and Taiwan.
- Competing with them requires significant resources and strategic planning.
- The semiconductor sector also depends on continuous innovation and research, but Bangladesh lacks adequate R&D facilities and funding, limiting the industry’s ability to innovate and stay competitive.
Possible Solutions
To address these challenges, Bangladesh needs targeted solutions.
- Developing a skilled workforce through collaboration with universities to create specialized semiconductor programs and offering training and scholarships can attract and retain talent.
- Securing substantial investment by providing tax breaks and subsidies for semiconductor startups and encouraging private-public partnerships can help share the financial burden.
- Creating attractive conditions for foreign direct investment by reducing bureaucratic hurdles is also crucial.
- Improving infrastructure by upgrading ports, airports, and transport systems will ensure quick and efficient movement of raw materials and finished products.
- Developing dedicated tech parks with state-of-the-art facilities for semiconductor companies can further support the industry.
- Focusing on innovation and research by establishing R&D centers with government and private funding and promoting collaboration between academia and industry can drive technological advancements.
- Implementing strong policy support through clear, investor-friendly policies and performance-based incentives for local companies can create a stable regulatory environment and build investor confidence.
Conclusion
Bangladesh’s semiconductor industry has promising future possibilities. With strategic investments and policy support, the country could earn $10 billion from the semiconductor industry. The growing demand for electronics offers a significant market for local manufacturers, and export potential is high.

