Bangladesh, a nation known for its resilience, is currently navigating a complex economic landscape brimming with challenges and promising opportunities. The funds repatriated by Bangladeshi expatriates working abroad, commonly referred to as remittances, play a pivotal role in sustaining the nation’s economy. Given that remittances serve as a linchpin for both economic stability and the well-being of numerous households, their significance to the country’s economic health cannot be overstated. However, it is imperative for Bangladesh to reevaluate its approach to bolstering long-term economic resilience in light of shifting remittance trends and evolving global dynamics.
Over the years, Bangladesh’s economy has experienced substantial gains thanks to remittances. A considerable number of Bangladeshi expatriates are gainfully employed in various regions, including Southeast Asia, the Middle East, Europe, and North America. Their earnings serve as a lifeline, supporting their families, financing education, and expanding personal opportunities.
The cumulative impact of remittances on the nation’s economy has been transformative. They have elevated living standards, alleviated poverty, and widened access to healthcare and education for countless Bangladeshi households. Today, millions of individuals enjoy financial security and are less susceptible to economic downturns, all thanks to the enduring flow of remittances.
Bangladesh’s Economic Achievements
A few days ago, At the Public Finance Management (PFM) Summit 2023, Finance Minister AHM Mustafa Kamal highlighted Bangladesh’s economic progress, including becoming the 34th-largest economy globally, with a GDP size of $454 billion compared to $91 billion in 2008. The average GDP growth rate increased from 5.8 percent (2002-2008) to 6.6 percent (2009-2022), and per-capita national income grew from $760 to $2,765. The government also created millions of jobs both domestically and abroad.
The Crucial Role of Remittances
In recent times, remittances have become a crucial economic factor in Bangladesh, impacting economic growth, balance of payments, foreign exchange reserves, national savings, and the velocity of money. For approximately two decades, remittances have accounted for approximately 35% of export earnings. Furthermore, they surpass foreign aid in significance, reducing the nation’s reliance on such aid. Remittances have gained momentum in Bangladesh, emerging as the second-largest source of foreign currency earnings after the garment sector. When the cost of imported raw materials is subtracted from the garment sector’s foreign currency earnings, it becomes the largest contributor to foreign currency earnings. While remittance earnings continue to rise, they are doing so at a slower rate compared to the increasing number of emigrants from Bangladesh, primarily composed of unskilled or semi-skilled laborers rather than professionals in international migration. The percentage of remittances in Gross National Income (GNI) is steadily increasing, positively impacting nearly all of the country’s macroeconomic indicators. Despite the drawbacks associated with remittances, such as brain drain, their overall contribution to Bangladesh’s economy remains highly effective.
Remittances have always played a pivotal role in Bangladesh’s economy. However, recent trends indicate a gap between the increasing number of expatriate workers and the remittance inflow.
The Remittance Inflow of Bangladesh
In June, remittance increased to $2.2b
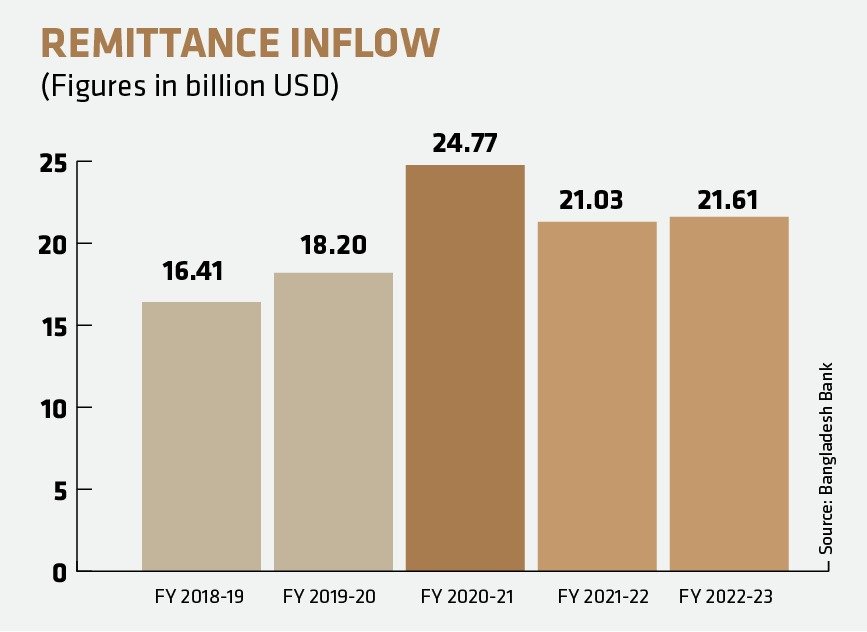
Remittance Growth Statistics of Bangladesh Over the Years
Bangladesh’s economy heavily depends on expatriate earnings, which represent the second-largest source of foreign currency earnings. During January-March 2023, there was a significant increase (14.97 percent) in remittance inflows as expatriates sent more money home in anticipation of Ramadan and major festivals, despite the world’s ongoing struggle with high inflation. Furthermore, the government and Bangladesh Bank’s fiscal incentives and domestic monetary policies have played a crucial role in restoring the positive trend in remittance inflows.
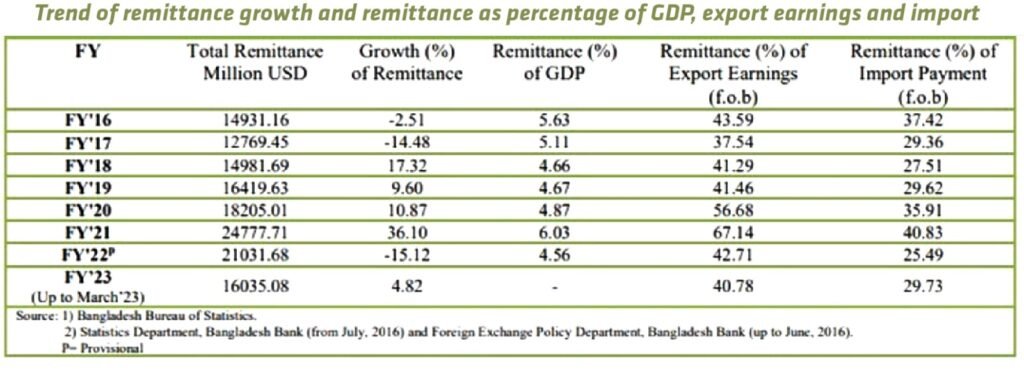
The cumulative total remittance inflow for the period of July-March in FY’23 reached USD 16,035.08 million, which was 4.82 percent higher than the USD 15,298.26 million received during the same period in FY’22. The inflow of remittances and its percentage contributions to GDP, exports, and imports, which faced significant setbacks in FY’22 due to the COVID-19 pandemic, are expected to rebound positively in the current fiscal year.
Measures Taken by the Government and the Bangladesh Bank
The Bangladesh government and Bangladesh Bank have implemented various measures to boost remittance inflows through the banking channel. These measures aim to simplify the process and provide incentives for foreign remittances sent through official channels.
One significant initiative was the introduction of a 2 percent cash incentive for the first time on foreign remittances sent through the banking channel, effective from July 1, 2019. This cash incentive was increased to 2.5 percent starting from January 1, 2022. Notably, this incentive extension was also granted to United Nations peacekeeping mission officials from the army, navy, air force, and police, who are engaged in missions worldwide.
To streamline the procedure for disbursing cash incentives, Bangladesh Bank issued instructions to banks. These instructions included the requirement for remitters’ documents to be submitted to their respective banks by the sender’s bank. The sender’s bank would verify these documents and confirm to the receiver bank, allowing for the quick release of cash incentives. In cases where the sender bank and receiver bank are the same, the receiver bank would collect and verify the documents independently.
Another essential step was the submission of Wage Earners’ Remittance data through a Rationalized Input Template (RIT), with the statement of money paid provided on a monthly basis. This submission follows a specific form for the 2 percent cash incentive for inward remittances through formal channels.
These measures represent the government and Bangladesh Bank’s commitment to encourage the use of formal banking channels for foreign remittances. The cash incentives and simplified procedures aim to make it more attractive for individuals to send remittances through official channels, ultimately benefiting the country’s economy. The 2 percent cash incentive was initially introduced in 2019, and it was increased to 2.5 percent in 2022. Furthermore, the extension of the cash incentive to United Nations peacekeeping mission officials enhances the appeal of sending remittances through banking channels. To expedite the process, guidelines were provided to banks, emphasizing document verification and a streamlined confirmation process between sender and receiver banks.


