Despite severe Western sanctions aimed at crippling Russia’s economy and halting its military actions in Ukraine, the nation’s GDP grew by a surprising 3.6% in 2023 and is projected to expand by 2.6% in 2024.
This resilience can be attributed to high oil prices and increased military spending. Russia has strategically strengthened trade ties with non-Western nations like China and India while establishing parallel markets to circumvent sanctions. Through these measures, the Russian economy has maintained steady growth despite global economic pressures.
You Can Also Read: RUSSIA’S NUCLEAR GAMBLE: A STEP TOO FAR?
Background
Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in February 2022 prompted a coordinated global response, with sanctions imposed by the United States, European Union, United Kingdom, and other allied nations. These measures aimed to cripple Russia’s economy and diminish its ability to wage war. The U.S. imposed severe limitations on Russia’s largest banks, state-owned enterprises, and elites.
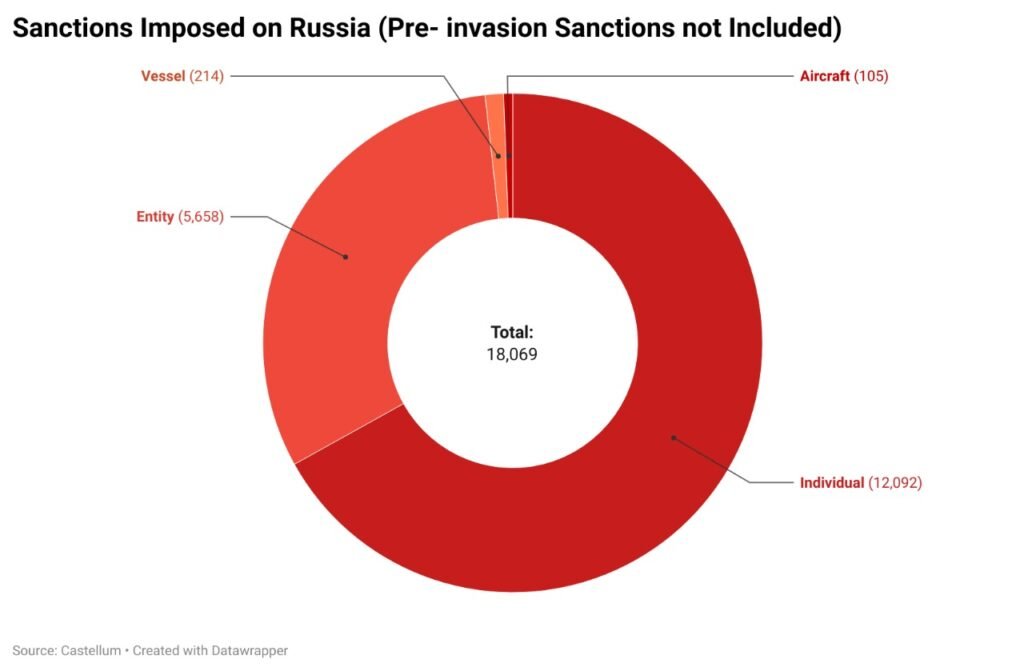
The EU followed suit with multiple sanction packages, expanding restrictions to third-country entities assisting Russia’s military efforts. Nonetheless, Russia adapted by strengthening trade ties with non-Western countries and establishing parallel markets to mitigate the impact of these sanctions. Russia is currently the most sanctioned country in the world, with pre-invasion and post-invasion sanctions totaling more than 20,000.

Current Status of Russian Sanctions
As of May 2024, the Western world has imposed far-reaching sanctions on Russia, targeting critical industries like finance, energy, and military sectors. The United States and its allies have sanctioned over 20 jurisdictions, introducing more than 300 new measures designed to disrupt Russia’s military-industrial capabilities and hinder its ability to fund the war in Ukraine. These actions encompass asset freezes, export controls, and prohibitions on investments in key Russian economic sectors.
The European Union has been equally proactive, implementing its 13th package of sanctions. This latest round focuses on preventing circumvention and includes restrictions on companies from third countries involved in aiding Russia.
The EU has tightened export restrictions and due diligence requirements for businesses to prevent sanctions evasion, extending these measures to sectors such as software, engineering, and manufacturing.
The United Kingdom has joined forces with the EU and the U.S. in expanding sanctions. Recent measures have targeted Russian oil, with the U.K. specifically aiming to stop the trade of Russian oil through intermediaries in the United Arab Emirates. Additionally, the U.K. has sanctioned entities in the Russian energy and diamond industries.
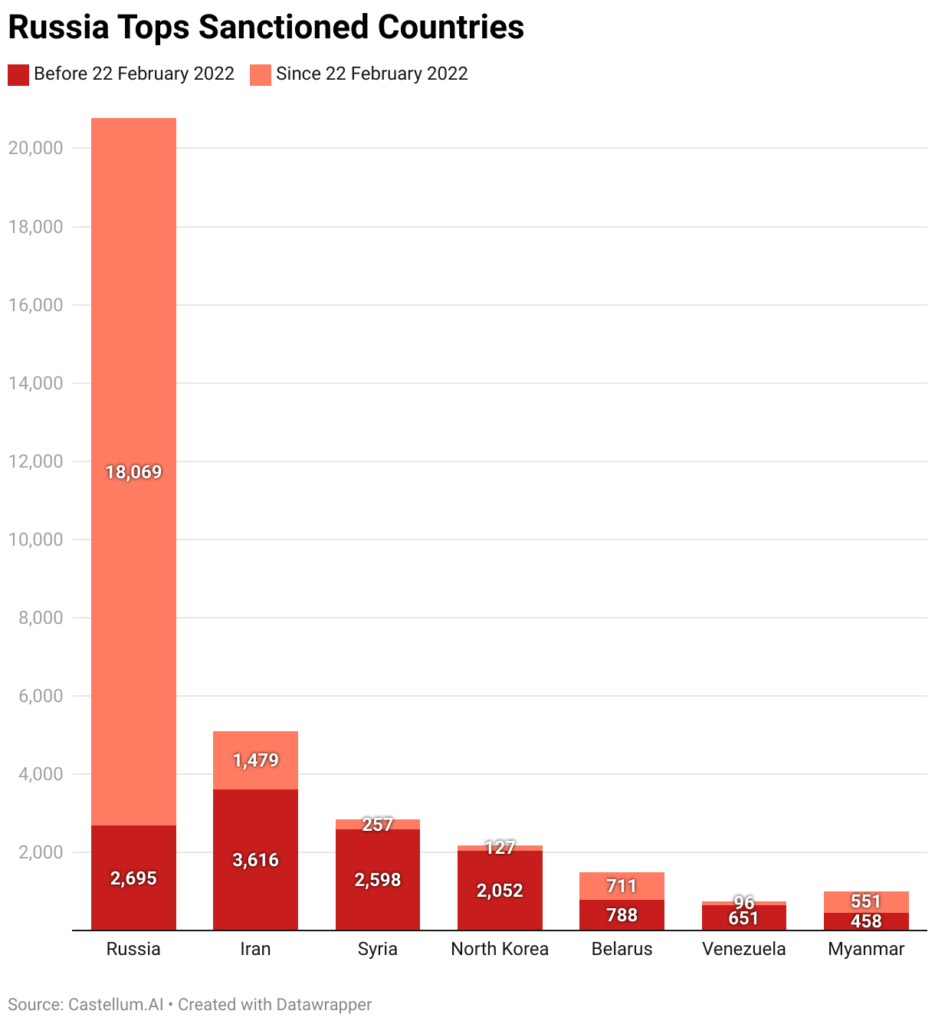
Despite these comprehensive sanctions, Russia has adapted by strengthening trade ties with non-Western countries. Nations like China, India, and Turkey have become key partners, helping Russia bypass some of the restrictions imposed by the West. This strategic adaptation has allowed Russia to maintain a degree of economic stability and continue funding its war efforts.
While the sanctions have undoubtedly imposed significant economic costs on Russia, they have not yet achieved their primary goal of crippling the Russian economy entirely. The country’s strategic partnerships and internal adjustments have mitigated the full impact of these measures to a certain extent.
Russia’s Projected Growth Rate (Before and After Ukraine Invasion)
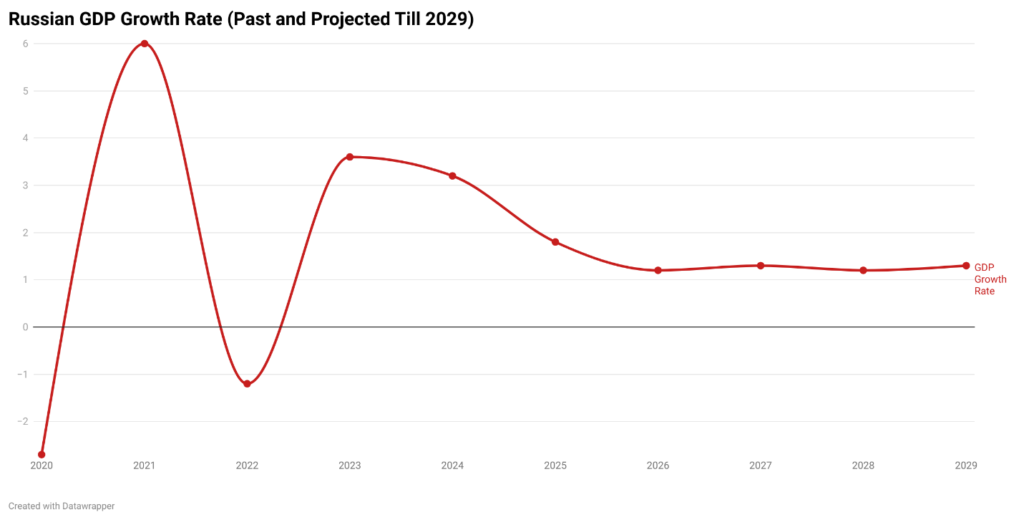
Before the invasion of Ukraine, Russia’s economy maintained a stable footing, with the GDP growth rate registering at 4.7% in 2021. However, the landscape shifted drastically following the invasion in February 2022, as the ensuing sanctions and the escalating war efforts significantly impacted Russia’s economic outlook.
In the immediate aftermath of the invasion, Russia’s growth rate declined to negative in 2022, reflecting the consequences of the imposed sanctions and the nation’s increasing economic isolation.
Nonetheless, Russia’s GDP remarkably grew by 3.6% in 2023, buoyed by the favorable conditions of high oil prices and increased military spending. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) projects a 2.6% growth rate for Russia in 2024, a figure that surpasses the projections for many G7 nations, underscoring Russia’s resilience in the face of adversity. While the sanctions undoubtedly impacted key sectors of the Russian economy, the nation has demonstrated a remarkable ability to adapt.
Russia Adopted and Succeeded to Circumvent Sanctions
Russia has adeptly maneuvered around Western sanctions imposed following its invasion of Ukraine. The country employed various tactics to maintain economic stability and continue military operations.
- Importing Essential Components: Russia bypassed sanctions by importing crucial components through third countries. In 2023, it imported over $1 billion worth of microchips from the U.S. and EU via nations like China, Turkey, and the UAE. These microchips are essential for both civilian and military applications.
- Parallel Markets and Networks: Russia utilized parallel markets to continue trade. It established networks of intermediaries and shadow fleets to transport oil and other commodities. This network allowed Russia to sell oil globally despite sanctions intended to restrict its energy exports.
- Financial Innovations: Russia adopted financial innovations to circumvent sanctions. It used virtual assets and blockchain technology to facilitate transactions outside traditional banking systems, enabling sanctioned entities to continue operating globally.
- Trade with Non-Western Countries: Russia strengthened trade relationships with non-Western countries. China, India, and Turkey became crucial trading partners, helping Russia mitigate the impact of Western sanctions. These countries provided essential goods and services, ensuring a steady supply chain.
- Domestic Production and Self-Reliance: Russia increased domestic production of critical goods, reducing dependency on Western imports and bolstering self-reliance. The country also stockpiled essential items to cushion against supply chain disruptions.
These measures have allowed Russia to maintain economic activity and support its military efforts despite extensive sanctions. The strategies underscore the complexity of enforcing sanctions and the resilience of targeted economies.
Sanctions Have United Russians
Sanctions have played a vital role in uniting Russia internally. The Russian government has utilized these sanctions to cultivate a sense of nationalism among its citizens. The population is encouraged to support local products and reduce reliance on foreign goods, leading to increased domestic production and creating a sense of resilience and self-sufficiency.
State media portrays the sanctions as an attack from the West, reinforcing the narrative of an external enemy. This narrative has effectively rallied public support for the government and its policies. Additionally, the government has incentivized local businesses to fill the gaps left by departing Western companies, further bolstering domestic industries.
Speculation and Projection
Despite its resilience, Russia’s economy faces considerable challenges. The IMF predicts a growth rate of 1.1% for 2024, which is lower than previous forecasts. Increased defense spending puts a strain on the budget, and future economic stability heavily depends on oil prices and trade with non-Western countries.
The reliance on a few key trading partners like China increases Russia’s vulnerability. Economic isolation may limit technological advancements and overall growth potential. As sanctions persist, Russia must strike a balance between sustaining military efforts and ensuring economic stability.
Conclusion
Russia’s economy has undoubtedly suffered from the consequences of sanctions. However, the sanctions have not managed to cripple or halt the growth. Instead, it has had the effect of pushing Russia closer toward China, India, Iran, North Korea, and other partners.
The consequences of this are not isolation, but belligerence. By pushing Russia closer to these nations, the Western powers have inadvertently widened the bridge toward rapprochement. It, however, must be stated that Russia’s invasion of Ukraine left the Western powers with very few options other than to impose sanctions.
Russia has managed to withstand extensive sanctions through strategic adaptations. However, its reliance on key trade partners and high military spending poses future risks. Sustaining economic stability will require balancing these factors amid ongoing geopolitical tensions and internal economic pressures.


