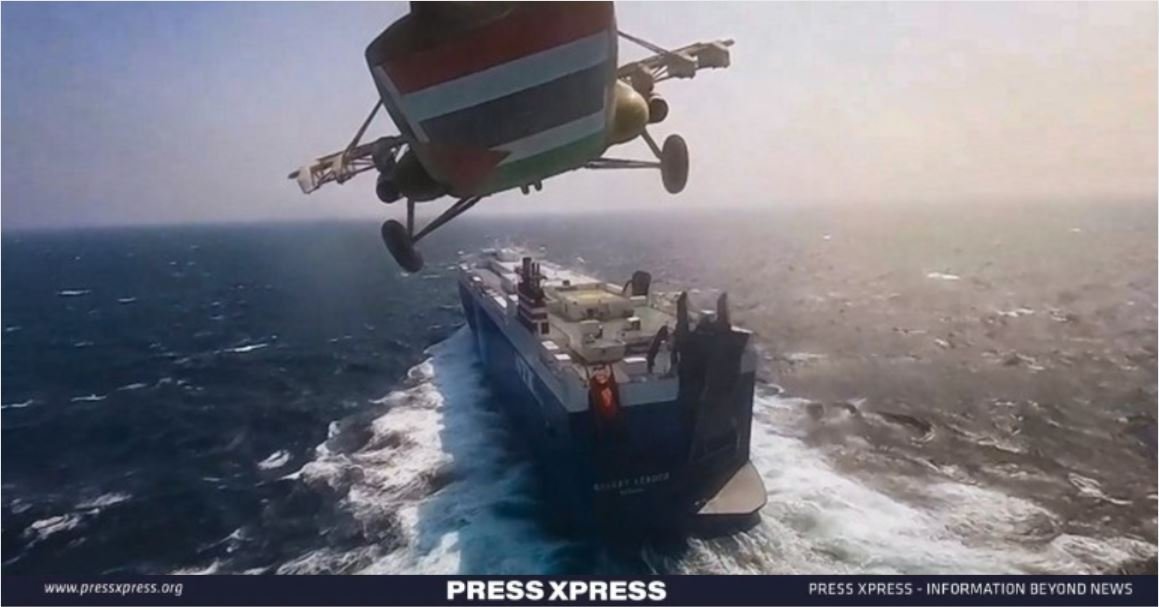
The Red Sea, a vital global trade route, faces escalating tensions due to attacks by Yemen’s Houthi rebels, particularly since November 2023, amid the broader Israel-Hamas conflict. The strategic Bab-el-Mandeb Strait has seen over 60 attacks, forcing shipping companies to reroute around South Africa, increasing costs, and disrupting global trade.
You can also read: Russian Forces Gain Foothold in Niger’s Former U.S. Military Base
These disruptions, compounded by challenges like the Ukraine war and climate-induced changes in the Panama Canal, further strain international shipping and supply chains. The UN Security Council has condemned the attacks, emphasizing the need for freedom of navigation, while the U.S. and UK have intensified military actions to secure the area, highlighting the complex interplay of regional conflicts and global trade.
Houthi Attacks Intensify
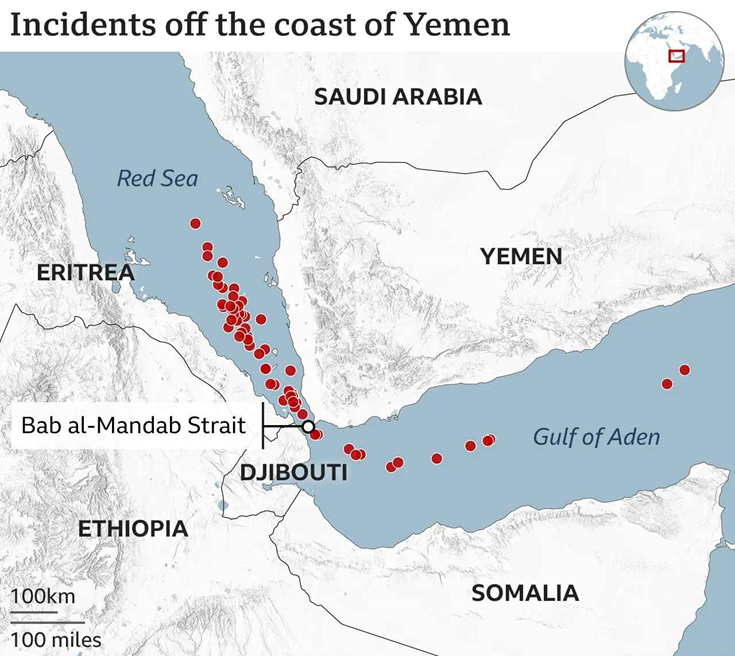
Since November 2023, Houthi attacks in the Red Sea have dramatically increased. These assaults, often targeting commercial vessels with ties to Israel, have severely disrupted essential maritime trade routes. The Houthi rebels, aligned with Iran, have expanded their targets to include the U.S. and other international shipping, causing major disruptions to global shipping operations.
The situation in the region remains unstable, with U.S. and UK forces actively engaging Houthi targets in response to the ongoing threats. Despite these efforts, the attacks continue, contributing to heightened tensions and the risk of a broader regional conflict.
Disruption of Global Trade
The United Nations Security Council has demanded an immediate end to these attacks and stressed the importance of complying with international maritime laws.

The economic consequences of these disruptions are substantial. Shipping routes are being diverted to avoid high-risk areas, significantly increasing transit times and costs. This rerouting affects global supply chains, especially energy supplies and shipping costs. The increased operational costs are being passed on to consumers, with some shipping rates rising dramatically.
Moreover, the ongoing instability in the region has put global trade networks on high alert, with businesses and governments preparing for prolonged disruptions. This situation highlights the interconnected nature of global trade and the far-reaching impact of regional conflicts on international economic stability.
Houthi Influence and Popularity Amid Red Sea Attacks
The Houthi movement in Yemen has experienced a rise in both popularity and influence due to its ongoing maritime attacks in the Red Sea. These attacks, which escalated in November 2023, have not only disrupted global shipping but also established the Houthis as a major power broker in the region.
Initially, these maritime assaults were declared as acts of solidarity with the Palestinians against Israeli policies. This stance has struck a chord within certain segments of Yemeni society and the broader region, portraying the Houthis as defenders of Palestinian rights. This narrative has been successful in rallying public support among local populations and certain groups across the Middle East who view the Palestinian cause as crucial.
The growing popularity of the Houthis is evident in large-scale rallies and public gatherings in their controlled territories, where participants often express support not only for the group’s actions against international shipping but also for their role in the broader regional conflicts. Such public displays of support have given the Houthis a semblance of legitimacy and have helped them recruit more fighters and supporters to their cause.
The Houthis have used this newfound influence to strengthen their political position within Yemen. By presenting themselves as champions of the anti-Israel cause, they have managed to shift focus away from their governance challenges, such as economic mismanagement and alleged human rights abuses. This narrative shift has allowed them to consolidate power, especially in regions under their control, and to assert more authority in negotiations with both local and international actors.
Internationally, the Houthis’ actions have compelled major global powers to engage with them as a serious political and military force. Despite widespread condemnation of their tactics, any resolution to the conflict in Yemen now seems to require some level of negotiation with the Houthis. This has given them a substantial platform to influence regional politics, far beyond what might have been expected for a non-state actor.
The tactical use of maritime attacks has also had implications for regional diplomacy. The Houthis’ ability to threaten one of the world’s busiest maritime routes has forced neighboring countries and global powers to reconsider their strategies in the region. Saudi Arabia, for instance, has been involved in direct talks with the Houthis, partially driven by the desire to mitigate threats to maritime security that affect its economic interests.
In conclusion, the Houthi attacks on Red Sea shipping have altered the Middle East’s geopolitical dynamics and posed major challenges to global trade. Diplomatically, the situation remains tense, with the international community urging restraint and seeking peaceful resolutions. The US has engaged in indirect talks to de-escalate tensions, while regional powers and international bodies remain on high alert.
As these attacks continue, the international community focuses on pressuring the Houthis while exploring diplomatic avenues to ensure the safety of Red Sea shipping lanes and regional stability. The outcome will have far-reaching implications for regional politics and the global economy.


