China has announced an increase in its 2024 defense budget, as part of its strategic goal to enhance military capabilities. While China claims its military spending is modest relative to its GDP, some experts suggest that actual spending could be higher, as significant defense-related portions are not included in the official budget.
Economically, China has set a growth target of around 5% for the coming year, following a period of recovery. Early 2024 trade figures show signs of recovery, with increases in exports and foreign investments, despite challenges in the property market and geopolitical tensions.
You can also read: Space Arms Race Stalls Due to Russia’s Veto
However, transparency issues persist, with domestic and international observers calling for greater clarity in China’s economic data reporting. Recent changes to statistical methods and suspensions in reporting certain indicators have sparked debates about the accuracy and reliability of the published data. These developments occur as China asserts its regional and global influence, balancing economic strategies with military advancements.
Defense Spending
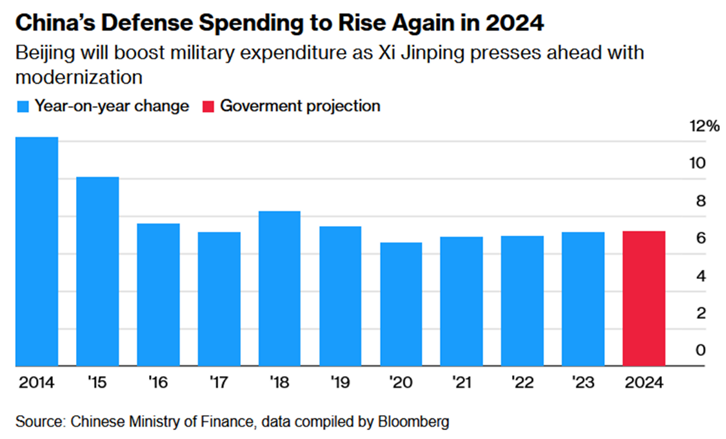
Recent Increases
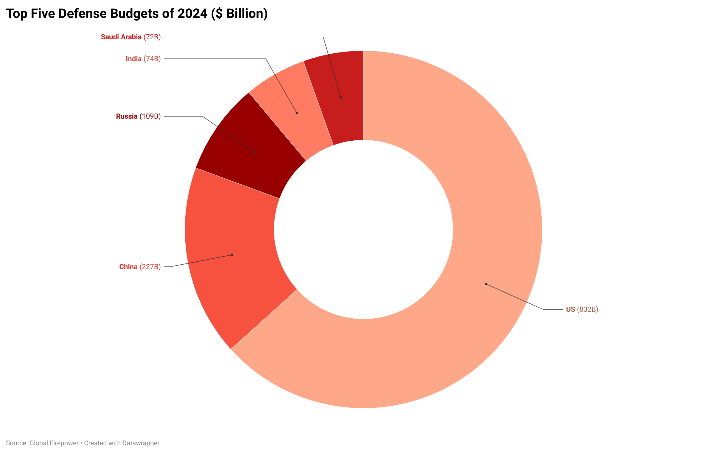
China’s defense budget for 2024 demonstrates a 7.2% increase, reaching 1.7 trillion yuan ($236.1 billion). This marks the third consecutive year with a rise exceeding 7%, reflecting the country’s ongoing strategic investments in its military capabilities. Despite these consistent increases, China asserts that its military spending, when considered as a percentage of its GDP, remains comparatively low in relation to other major global powers.
Transparency Concerns
Some experts argue that China’s reported defense budget does not provide a comprehensive account of all military-related expenses. They suggest that additional expenditures, such as costs associated with the country’s space program, provincial military bases, and veteran benefits, are not publicly disclosed within the official budget figures. The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute has estimated that China’s actual military spending could be as much as 27% higher than the officially reported number, raising concerns about the transparency and accuracy of the available data.
Economic Performance

Growth Projections and Realities
China has set its GDP growth target at around 5% for 2024. This follows a year where growth slightly exceeded expectations, reaching 5.2%. However, the IMF predicts a more modest growth of 4.6% due to ongoing challenges in the property sector and other economic pressures. These projections reflect China’s gradual recovery from the economic disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.

Trade and Investment
Early 2024 showed an increase in China’s exports and the establishment of foreign-funded enterprises, signaling a potential resurgence in economic activity. Exports rose by 10.3% in the first two months, and the setup of new foreign enterprises increased by 74.4% compared to the previous year. Despite these positive signs, the property market continues to struggle, affecting overall economic stability and growth expectations.
China is actively working to enhance its trade relationships and attract more foreign investment. Recent policy adjustments aim to improve the business environment and restore investor confidence shaken by previous economic uncertainties and regulatory challenges. These efforts are crucial as China navigates complex global economic conditions and strives to maintain its growth trajectory.
Data Transparency and Reliability
Criticisms and Calls for Improvement
China’s approach to economic data reporting has faced criticism for lack of transparency. Recent adjustments and suspensions in the reporting of certain economic indicators, such as the youth unemployment rate, have raised concerns about the reliability of the data. These changes have sparked debate. What is very unique about the debates is that critics are both international observers and domestic Chinese.
Experts and economic advisors within China have called for more comprehensive data releases. They argue that richer, more detailed statistics from diverse sources would enhance transparency and bolster investor confidence. This includes urging the government to allow more releases from independent research institutions and industry associations.
China’s Youth Unemployment Data and Transparency Concerns

After a six-month hiatus, China restarted publishing youth unemployment data in January 2024, employing a revised statistical approach. The National Bureau of Statistics of China had suspended the release of these figures in June 2023, when youth unemployment reached an all-time high of 21.3 percent following years of consecutive increases.
The bureau’s spokesperson stated that the methodology for calculating age-specific unemployment rates required refinement, necessitating a temporary publication halt. Under the new methodology, which excludes university students, the youth unemployment rate stood at 15.3 percent in March 2024.
China’s choice to cease publishing its monthly youth unemployment statistics; then resume it with a ‘revised calculation method’ has raised questions about data transparency and the potential economic consequences. These crucial numbers are essential for economists and investors to precisely assess the extent of China’s economic downturn.
Impact on Investor Confidence and Policy Making
The opacity in China’s economic data can deter foreign investment and complicate policymaking. Without reliable data, investors may hesitate to commit capital, fearing unforeseen risks. Similarly, policymakers require accurate statistics to craft effective economic strategies. Enhancing data transparency is seen as essential for stabilizing financial markets and guiding long-term economic planning.
Efforts to improve data richness and frequency are underway, aiming to address these challenges and provide a clearer picture of China’s economic landscape. These steps are crucial as China seeks to maintain its economic growth and navigate global market dynamics.
Strategic Implications
Military and Economic Goals
China’s defense strategy is closely intertwined with its broader national objectives, including economic ambitions and regional influence. The increase in military spending aligns with China’s goal of establishing itself as a formidable regional and global military power by 2027, as part of the ‘double centennials’ strategy. This strategy marks significant anniversaries of the Communist Party and the People’s Republic of China. China’s military modernization encompasses expanding its nuclear arsenal, enhancing cyber capabilities, and improving space warfare capacities.
Regional Stability and Global Influence
China’s military growth significantly impacts its regional relationships, particularly in the Indo-Pacific. With increased military capabilities, China can assert greater control over contested areas like the South China Sea and bolster its position towards Taiwan. This projection of power aims to secure China’s economic and political interests beyond its immediate borders, shaping global trade routes and international diplomacy.
Conclusion
China’s strategic posture combines military modernization with economic assertiveness to shape a global role aligned with its national interests. The recent defense budget increase and emphasis on technological and strategic capabilities aim to support its regional ambitions and broader global influence.
Despite global economic pressures and domestic challenges, China has maintained growth of around 5%, supporting its military expansion and enhancing its geopolitical weight. This dual-use strategy of economic and military development has profound implications for global security, reshaping China’s international relationships and affecting global power dynamics.
As China pursues its goal of becoming a leading global power, its strategies will likely prompt varied responses from other nations, influencing global economic patterns, security policies, and diplomatic relations.


