Key Takeaways:
- The EU passed the world’s first Artificial Intelligence (AI) Act on March 13, 2024
- UNESCO released its ‘Recommendation on the Ethics of Artificial Intelligence’ in 2022
- The United States has a non-binding ‘Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights’
- Bangladesh introduced its National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence in 2020
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a central element in global technological advancement, with particular importance for developing nations like Bangladesh. The need for transparency and accountability in AI systems is paramount to prevent potential harm and ensure fair practices. Bangladesh faces unique challenges in managing AI, combating false information, and maintaining accountability.
You can also read: AI Revolution: Boon or Economic Armageddon?
AI systems generate predictions and can perform actions that may be immoral or unlawful if left unchecked. Accountability mechanisms ensure that AI systems adhere to ethical principles and operate fairly. Transparency in AI processes helps eliminate bias and discrimination in decision-making, thus improving overall trustworthiness.
On March 13, 2024, the European Union (EU) passed the world’s first Artificial Intelligence (AI) Act, marking a milestone in AI regulation. This development highlights the growing global recognition of AI’s impact and the need for formal governance structures. For Bangladesh, a country experiencing rapid technological growth, AI presents both opportunities and challenges.
As Bangladesh aims to use AI for societal progress and economic development, the establishment of a comprehensive legal framework becomes essential. This framework would govern AI-related issues, ensuring that the technology’s benefits are maximized while potential risks are mitigated. The creation of such regulations will be crucial in shaping Bangladesh’s future relationship with AI technology.

The Importance of AI Laws in Bangladesh
AI laws in Bangladesh are essential for managing the rapid growth of artificial intelligence technologies. The country’s digital landscape has expanded, with internet penetration reaching 74.4% in 2023, according to the Bangladesh Telecommunication Regulatory Commission. This growth increases the potential impact of AI on society and the economy.
The importance of AI laws in Bangladesh stems from several factors. First, they provide a framework for ethical AI development and use. Without proper regulations, AI systems may perpetuate biases or be used for harmful purposes. Laws can establish guidelines for fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI applications.
Second, AI laws can protect citizens’ rights and privacy. As AI systems collect and process large amounts of personal data, regulations are needed to ensure data protection and prevent misuse. Bangladesh’s Personal Data Protection Act, currently in draft form, aims to address these concerns.
Third, AI laws can foster innovation while mitigating risks. Clear regulations provide a stable environment for businesses and researchers to develop AI technologies. This can attract investment and promote economic growth in the tech sector.
Fourth, AI laws can address the issue of disinformation, which is a growing concern in Bangladesh. Regulations can set standards for AI-generated content and establish mechanisms for fact-checking and content moderation.
Lastly, AI laws can help Bangladesh align with global standards and participate in international AI governance discussions. This is crucial for the country’s digital integration with the global economy.
Global Perspectives on AI Regulation
Global perspectives on AI regulation vary, with different approaches emerging across regions. UNESCO released its ‘Recommendation on the Ethics of Artificial Intelligence’ in 2022, emphasizing AI transparency and responsibility in respecting human rights and ethical principles. On March 13, 2024, the organization also passed the world’s first Artificial Intelligence (AI) Act. This document guides member states, the EU, and stakeholders on ethical considerations for AI policies and regulations.
The European Union leads with the world’s first comprehensive AI law, the AI Act. This legislation prioritizes data quality, transparency, human oversight, and accountability. It requires conformance assessment of high-risk AI systems and transparency for AI systems that interact with humans or generate deep fakes.
The United States adopts a different approach with its ‘Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights’. This non-binding guide protects against algorithmic discrimination, allows opt-outs from automated systems, and promotes transparency and fairness. Companies must explain AI decision-making and obtain consent before using consumers’ personal data.
China is drafting its AI law, focusing on promoting AI safety and innovation aligned with socialist values and public order. The regulation requires service providers to help users understand and apply AI content rationally. It includes penalties for violations, with fines ranging from 10,000 to 100,000 yuan.
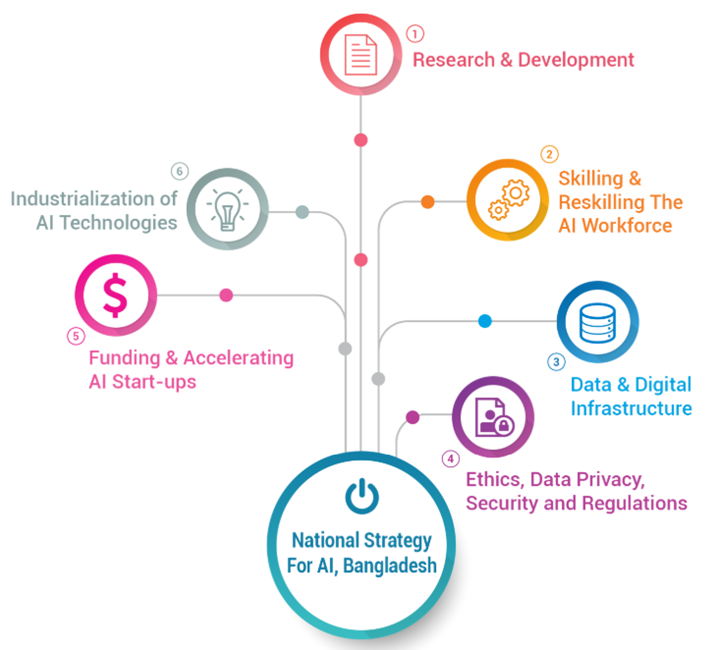
Bangladesh’s National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence (2020)
Bangladesh’s National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence, introduced in 2020, aims to address ethical issues and establish a legal and ethical foundation for AI development. The strategy focuses on fairness, cybersecurity, and transparency in AI systems. It promotes AI safety to reduce unintended harm from poorly designed systems and advocates for responsible AI governance.
The strategy outlines a national AI ecosystem with information frameworks and AI applications. It encourages legislation and policy formulation to create an ethical and legal framework for AI. The action plan assists policymakers in developing AI projects.
Despite its intentions, the strategy faces implementation challenges. Bangladesh lacks a legal AI technology governance framework and national policy. The country has AI technology professionals but lacks legal expertise in technology ethics, which complicates regulatory framework development.
The strategy emphasizes the need for AI safety, responsible governance, and transparency. The lack of a comprehensive legal framework and enforcement mechanisms hinders progress in AI regulation and ethical implementation.
To improve the strategy’s impact, Bangladesh needs to develop binding regulations, invest in legal expertise for technology ethics, and create mechanisms for enforcement and accountability in AI development and deployment.
Recommendations for Bangladesh
Bangladesh needs to implement several strategic measures to address the challenges posed by AI and disinformation. The government should prioritize the development of a comprehensive AI regulatory framework. This framework should build upon the National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence (2020) and incorporate clear guidelines for AI development, deployment, and use.
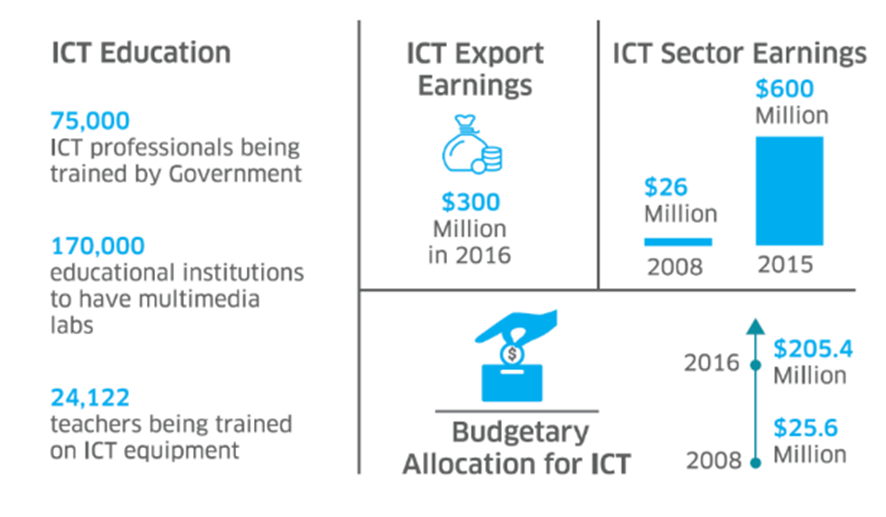
The Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics reports that only 5.6% of households have access to a computer. The government should invest in education programs that focus on critical thinking skills and media literacy. These programs should target both urban and rural populations to bridge the digital divide.
The government should establish a task force comprising technology professionals, legal experts, and ethicists to guide the development of AI regulations. This task force can draw insights from global best practices while tailoring solutions to Bangladesh’s specific context.
The current legal system lacks the capacity to handle complex AI-related cases. The government should invest in training programs for law enforcement and judiciary officials to enhance their understanding of AI technologies and related legal issues.
Bangladesh should actively participate in global AI governance initiatives and seek partnerships with countries that have advanced AI regulatory frameworks. This can facilitate knowledge exchange and help Bangladesh align its policies with international standards.
By taking these actions, Bangladesh can harness the benefits of AI while protecting its people from harm and misinformation. This approach can help the country use technology to counter false information while preserving democratic values and social unity. However, it’s important to remember that this is a complex issue that requires ongoing effort and international cooperation.


