The situation in Palestine remains deeply troubling, with the Israeli-Palestinian conflict intensifying and leading to severe humanitarian crises, especially in the Gaza Strip. The calls for Muslim unity in addressing these urgent issues have grown stronger, driven by the pressing need to alleviate the suffering of the Palestinian people and work towards a lasting peace.
The international community, including several Muslim-majority countries, has expressed deep concern over the unfolding crisis and has called for immediate action to support the Palestinian people in their time of need.
The Crisis and the Call for Unity

Recent reports depict a harrowing picture of the impact on the civilian population, with essential infrastructure, including hospitals and water systems, either destroyed or severely damaged. The humanitarian crisis has deepened, with a large number of people displaced within Gaza, struggling to access basic necessities and facing a suffocating blockade that severely limits the flow of aid and essential goods.
You can also read: From Vietnam to Gaza: US Campuses Reignite as Hubs of Anti-War Dissent!
In this context, the unity of the Muslim world could play a crucial role in advocating for peace and supporting vital humanitarian efforts in Palestine. Leaders from various Muslim countries have stressed the importance of solidarity and coordinated action in addressing the crisis, emphasizing the potential of united efforts to bring about meaningful change and rally global support for the Palestinian cause.
“If the Muslim Ummah works unitedly, it is possible to solve the Palestine crisis”
– Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina

In recent times, Muslim leaders have been making pressing calls for unity among Muslim nations to address the worsening crisis in Palestine. Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina of Bangladesh, while speaking at a gathering of the Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) in late 2023, emphasized that a collective effort from the Muslim Ummah is essential for resolving the Palestine issue. She noted that unity among these nations could have a substantial impact on global diplomatic dynamics and help support Palestinian sovereignty.
This sentiment is shared by various leaders and intellectuals who recognize that the divided stance of Muslim countries, often due to differing political and economic interests, has hindered effective support for Palestine.
Sayed Fared Alatas, a professor specializing in Muslim intellectualism, criticized the OIC’s inability to form a unified policy against Israeli actions, despite the severe humanitarian implications witnessed in Gaza. He called for a stronger, more united approach that could potentially compel influential nations to reconsider their positions and support for Israel.
The path forward is complicated by a complex web of political and economic interests that often divide Muslim nations. However, the urgency of the situation demands that these differences be set aside in favor of a common goal – to alleviate the suffering of the Palestinian people and work towards a just and lasting peace in the region.
Importance of Unity
The unity among Muslim nations holds immense importance, with far-reaching implications for their collective influence in global politics and their ability to support the Palestinian cause. When Muslim countries stand together, speaking with one voice, they can more effectively advocate for peace and justice on the international stage, ensuring that the plight of the Palestinian people is not overlooked or brushed aside.
This unity also allows for a more coordinated and efficient approach to delivering humanitarian aid and managing crises in conflict zones like Gaza. By pooling their resources and expertise, Muslim nations can provide more comprehensive support to those in need, alleviating suffering and working towards long-term solutions to the underlying issues that perpetuate the conflict.
Moreover, the benefits of unity extend beyond the political realm, with significant economic advantages to be gained through collaboration and cooperation. By harmonizing their approaches and working together, Muslim-majority countries can stimulate trade and development, utilizing their advantageous geographical positions and abundant natural resources to boost regional stability and prosperity.
Challenges to Unity
The unity of Muslim nations in addressing the Palestine crisis is hindered by several key factors. First, the political and economic interests of Muslim-majority countries vary widely, affecting their ability to present a united front on international issues.
For example, Gulf states have substantial investments in Western countries, which can influence their diplomatic choices. This contrasts sharply with nations like Iran, whose policies often clash with Western interests, creating a complex web of competing priorities that can be difficult to untangle.

Second, internal divisions within the Muslim world also pose significant challenges to unity. These divisions, which can be based on sectarian, ethnic, or regional differences, have historically undermined collective action and hindered the ability of Muslim nations to speak with one voice. In some cases, these divisions have even escalated into conflicts, further fragmenting the unity necessary for addressing larger issues like the Palestine crisis.
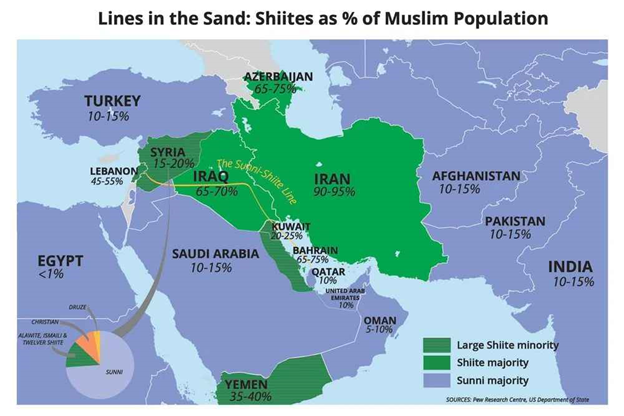
The Sunni-Shia divide has ancient roots, Over time, this evolved into a broader sectarian conflict, with Iran and Saudi Arabia emerging as the main representatives for Shia and Sunni Islam, respectively.
The sectarian divide is not just a religious or cultural issue but has far-reaching implications for regional politics. Countries with Sunni or Shia majorities often align with nations of the same sect, affecting international relations within the Muslim world. For example, Iran (Shia-majority) and Saudi Arabia (Sunni-majority) have supported opposing sides in conflicts across the Middle East, including Syria, Yemen, Lebanon and Iraq, based on sectarian affiliations, further dividing the Muslim community.
In many regions, the Sunni-Shia divide has fostered social divisions and sectarianism, which undermine the unity of Muslim communities at the local level. This division can lead to segregation, discrimination, and at times, sectarian violence.
The ongoing rivalry and conflict between Sunni and Shia groups have harmed the global image of Islam and affect how Muslim communities are perceived worldwide. It can also weaken the collective bargaining power of Muslim nations in international forums where unity could lead to more substantial influence.
Moreover, the effectiveness of organizations intended to unify Muslim nations, such as the Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC), has been called into question. The OIC has struggled to enforce unity or take effective action in conflict resolutions, including the Palestine issue. This has often resulted in resolutions that have limited practical impact, further eroding confidence in the organization’s ability to drive meaningful change.
Lastly, external influences and pressures can also detract from unity among Muslim nations. International relations, especially alignments and dependencies on powerful non-Muslim countries, can dictate the foreign policies of Muslim nations, sometimes in ways that are at odds with the collective interests of the Muslim world. This can create a complex balancing act for Muslim leaders, who must navigate competing demands and priorities while trying to maintain a united front.
Conclusion
As the Palestine crisis continues, the importance of unity within the Muslim world has never been more apparent. By coming together and speaking with one voice, Muslim nations can amplify their influence on the global stage, enhancing their diplomatic leverage and garnering much-needed international support for the Palestinian cause.
The path forward may be challenging, but the rewards of unity are immeasurable. It is important to set aside differences and work towards a common goal. Only through unity and solidarity can the Muslim Ummah hope to make a meaningful difference in the lives of those who suffer and to build a brighter future for all.


