Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina’s focus on boosting trade between Bangladesh and India through their currencies reflects a strategic step towards achieving economic independence and fostering regional collaboration
Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina, during a sideline meeting with Indian External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar at the Munich Security Conference (MSC) 2024 in Germany, emphasized the importance of expanding trade between Bangladesh and India using their respective currencies.
You can also read: Bangladesh Leans Towards Yuan Trade
Foreign Minister Dr Hasan Mahmud briefed reporters after the leader’s meeting and underscored the significance of their opinions on conducting bilateral trade in their national currencies to reduce dependence on the US dollar.
The Bangladesh Prime Minister, who was in Munich for a three-day official visit to attend the conference, is scheduled to return to Dhaka on February 19, 2024.
“We can do our business through exchanges of Bangladeshi Taka and Indian Rupee. It has already started, but we have to expand it further so that we can increase our businesses,”
– Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina

Earlier, Bangladesh has signaled its intent to utilize the Chinese currency, the yuan, in its bilateral trade with China, the world’s second-largest economy and a significant trading ally of Bangladesh. This strategic decision underscores Bangladesh’s aim to broaden its foreign exchange reserves and lessen reliance on the US dollar, which has encountered growing hurdles due to US sanctions on Russia.
Why Is Bangladesh Moving Away From The Dollar?
Bangladesh’s decision to pivot away from the dollar stems from several key factors. Firstly, the country aims to reduce its dependency on the US currency to shield its economy from potential volatility associated with fluctuations in the dollar’s value. By diversifying its currency reserves, Bangladesh seeks to mitigate risks and ensure stability in its monetary system.
Relying less on the dollar can give the country more flexibility in conducting its monetary policy and trade negotiations, reducing its susceptibility to external influences.
Bangladesh may be motivated by geopolitical considerations, seeking to assert its independence and strengthen its position in international finance. Diversifying currency reserves can also offer strategic advantages in diplomatic relations, providing Bangladesh with more leverage in negotiations with global partners.
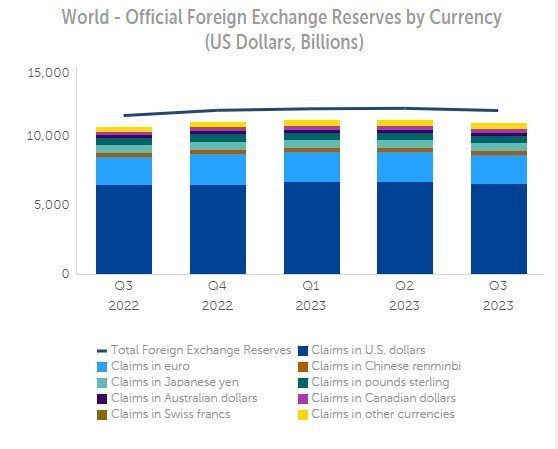
Bangladesh isn’t alone in its endeavor to distance itself from reliance on the dollar, which has historically held sway as the predominant reserve currency, medium of exchange, and unit of account within the global financial system.
The International Monetary Fund reports a decrease in the dollar’s share of global foreign exchange reserves, from 70% in 2000 to 60% in 2020, while the allocation to other currencies like the Euro, Yen, and Renminbi has grown.
Numerous nations are actively diversifying their reserves and exploring alternative currencies for trade settlements to mitigate exposure to the dollar’s volatility and associated risks, particularly amidst the backdrop of the US sanctions policy, often referred to as the ‘weaponization’ of the dollar.
US Sanctions Prompt Global Shift
The US has utilized its economic influence to enforce sanctions on nations it perceives as adversaries or violators of its interests, including Iran, Venezuela, North Korea, and Russia. By restricting their access to the dollar-based payment system, the US has effectively isolated them from the global economy and imposed significant trade and developmental costs.
Nevertheless, this new approach has boomeranged, prompting numerous nations to explore alternatives to the dollar and contest US financial dominance. For example, Russia has augmented its utilization of the yuan, euro, and other currencies for trade and reserves. This shift occurred after the US and its allies froze approximately $300 billion of Russia’s central bank funds and excluded its major banks from the SWIFT payment system in 2022, in response to its invasion of Ukraine. The US sanctions policy has also unsettled many other nations, which apprehend they could be the next targets of US reprisals, leading to doubts about the legitimacy and stability of the dollar-based system.
Rupee-Taka Bilateral Trade Benefits
Bangladesh, being a developing nation with a significant trade deficit with India, would find advantages in adopting the Taka-Rupee system for bilateral trade.
- Primarily, it would mitigate the expenses and uncertainties associated with converting the Bangladeshi Taka to the US Dollar and subsequently to the Indian Rupee, and vice versa.
- Moreover, it would foster accessibility and affordability of Indian goods and services, crucial for Bangladesh’s economic advancement.
- Additionally, it would strengthen the economic and diplomatic bonds between Bangladesh and India, bolstered by ongoing collaborative ventures like the Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar Economic Corridor and the India-Bangladesh Free Trade Agreement.
- Furthermore, it would diversify Bangladesh’s foreign exchange reserves, reducing its exposure to fluctuations in the dollar market and external shocks, while providing more flexibility in international transactions.
In conclusion, shifting away from the dollar reflects Bangladesh’s desire to foster stronger regional ties and promote the use of local currencies within South Asia, particularly among neighboring countries.


