The protection of data privacy is essential to Bangladesh’s progress toward becoming a Smart Bangladesh, as it allows for the creation of a safe and prosperous digital environment for everybody
The rapid digital transformation in Bangladesh has led to significant concerns regarding data privacy, particularly within the e-commerce sector. With the surge in internet and smartphone users, vast amounts of personal data are generated, leaving individuals vulnerable to privacy violations. Businesses in the e-commerce space, while benefitting from access to this data for targeted marketing, also face the responsibility of safeguarding it. Mishandling personal information can result in severe consequences such as identity theft and financial ruin, eroding trust in e-commerce platforms.
“In this fast-growing digital era, cybersecurity awareness must be introduced as part of the new social norms to the basic unit of the society, because it is no longer an option but a crucial necessity.”
– Bradley B. Dalina, Former Senior System Engineer at Afield Consulting Inc, Manila

The government’s efforts to address data privacy concerns include the drafting of the Personal Data Protection Act 2023 (PDPA), but there are lingering concerns about its effectiveness and alignment with international standards. A significant data privacy breach in July 2023 highlighted the vulnerability of even government websites, exposing millions of citizens’ personal details. This breach underscored the need for robust data security measures, comprehensive privacy laws, and public awareness initiatives to empower individuals to protect their data.
Addressing data privacy concerns requires a collaborative effort involving government authorities, human rights organizations, businesses, and the public. Implementing stringent regulations, raising public awareness, and providing education on digital rights are crucial steps toward ensuring data privacy in Bangladesh’s e-commerce ecosystem. Ultimately, protecting data privacy is essential for the country’s progress toward becoming a Smart Bangladesh, fostering a safe and prosperous digital environment for all citizens.
Data Privacy Risks: Bangladesh E-commerce
Possible risks of data privacy within the E-commerce Sector in Bangladesh are discussed below:
Lack of Regulatory Framework: Bangladesh’s e-commerce sector faces risk due to the absence of robust data privacy laws and regulations. Without clear guidelines, businesses may inadvertently mishandle customer data, leading to privacy breaches.
Cybersecurity Threats: E-commerce platforms are vulnerable to cyberattacks such as hacking, phishing, and malware. These threats can compromise sensitive customer information, including payment details and personal data.
Data Breaches: Data breaches pose a significant risk to e-commerce businesses in Bangladesh. Whether due to internal negligence or external cyber threats, breaches can result in the exposure of customer data, eroding trust, and damaging reputations.
Inadequate Encryption: Weak encryption practices leave customer data susceptible to interception and theft. Without proper encryption protocols, sensitive information transmitted over networks can be compromised, undermining data privacy.
Third-Party Risks: E-commerce companies often rely on third-party service providers for various functions, including payment processing and customer support. However, these partnerships can introduce additional data privacy risks if proper safeguards are not in place.
Insider Threats: Employees with access to customer data pose a potential risk to data privacy. Whether through malicious intent or inadvertent actions, insider threats can result in the unauthorized access or misuse of sensitive information.
Data Localization Requirements: Compliance with data localization laws can be challenging for e-commerce businesses operating in Bangladesh. Failure to store and process data within the country’s borders can lead to legal repercussions and jeopardize data privacy.
Lack of Awareness Among Consumers: Many consumers in Bangladesh may not fully understand the importance of data privacy or how their information is being used by e-commerce platforms. This lack of awareness can make them more susceptible to privacy violations.
Social Engineering Attacks: E-commerce platforms are vulnerable to social engineering tactics, where attackers manipulate individuals into divulging sensitive information. Phishing emails and fraudulent schemes can deceive users into disclosing personal data, compromising their privacy. Data Misuse: E-commerce companies may misuse customer data for purposes beyond what was originally consented to, such as targeted advertising or selling data to third parties. This misuse can violate trust and privacy expectations, leading to legal and reputational consequences
Bangladesh’s Data Privacy Crisis
In July 2023, Bangladesh faced a grave breach of data privacy when the website of the Office of the Registrar General, Birth & Death Registration inadvertently disclosed the personal details of millions of its citizens. This breach included unauthorized access to sensitive information like names, phone numbers, email addresses, and national ID numbers, exposing individuals to the dangers of identity theft, fraud, and various other malicious activities. The compromised data presents a significant risk, leaving citizens susceptible to targeted phishing attempts, spam, and harassment. Furthermore, this incident underscores the vulnerability of even governmental bodies to such breaches, raising questions about the measures that businesses can implement to address such threats. These breaches not only result in financial losses but also instill concerns about government surveillance and the potential misuse of personal data.

The Personal Data Protection Act 2023 (PDPA)
The cabinet of Bangladesh has given initial approval to the ‘Personal Data Protection Act-2023′ in 2023 aiming to enhance individual privacy and strengthen data management practices. The legislation, inspired by global frameworks like the EU’s GDPR, prioritizes informed consent for data collection and establishes a dedicated Bangladesh Data Protection Board. This board mirrors EU supervisory authorities and ensures compliance with regulations, reinforcing individuals’ control over their data. The act mandates registration for entities involved in data processing, promotes transparency, and outlines strict guidelines for data classification and sharing, including the potential inclusion of DNA information.
The Bangladesh Data Protection Board, with a designated chairman and four members, serves as the central authority for enforcement. It has the power to investigate complaints and impose fines up to Tk5 lakh, with foreign companies facing penalties of up to five percent of their total sales for violations. However, the draft law lacks provisions addressing AI-generated content, such as Deepfakes, which pose new challenges in content authenticity and misinformation prevention.
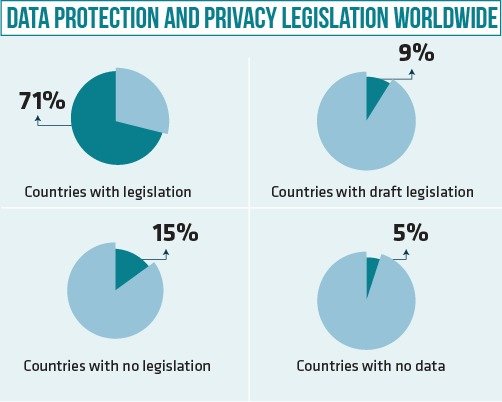
Despite this gap, Bangladesh’s proactive approach to data protection reflects its commitment to digital governance and citizen security. The ‘Personal Data Protection Act-2023’ aligns with global standards while tailoring regulations to suit local needs, setting an example for other nations in the realm of digital governance.
Recommendations for Data Privacy Measures in Bangladesh
Addressing data privacy concerns necessitates a multifaceted strategy encompassing various measures. Primarily, it is imperative to implement robust data security measures, including multifactor authentication and encryption protocols, across government organizations and businesses handling personal data. Additionally, establishing comprehensive privacy laws and regulations is vital to govern data collection, storage, and handling, thereby holding organizations accountable for breaches and promoting better data protection practices. Furthermore, empowerment through awareness is crucial, involving public awareness campaigns, workshops, and digital literacy programs to empower individuals to protect their personal information and exercise greater control over their digital identities.
Recognizing the collective responsibility of stakeholders in Bangladesh’s e-commerce ecosystem, including government authorities, human rights organizations, and the public, is paramount for ensuring data privacy. Inclusive legislation, developed with the active involvement of stakeholders, ensures compliance with international standards, creating an adequate legal framework safeguarding data privacy. Giving individuals maximal control over the collection, storage, processing, dissemination, and use of their data by public and private institutions is crucial for informed decision-making. Moreover, public awareness initiatives and education on moral values and digital rights are essential, as a knowledgeable and vigilant public plays a significant role in adequate data protection.
Concerns over data privacy in Bangladesh’s e-commerce sector highlight the necessity of an all-encompassing regulatory framework that complies with international standards of quality. Data privacy is ensured by raising public awareness, and protecting citizens’ data is a shared duty that multiple stakeholders at several levels of authority must participate in actively. The protection of data privacy is essential to Bangladesh’s progress toward becoming a Smart Bangladesh, as it allows for the creation of a safe and prosperous digital environment for everybody.