Key Highlights:
- Growth momentum slowed in Q4 2023
- 124 Chinese companies make their places on the Fortune 500 list
- China aims for a “world-class” military by 2035
- China introduced “wolf warrior” diplomacy
China is widely regarded as a rising power that poses a serious challenge to the United States and the existing international order. China has achieved remarkable economic growth, technological innovation, and military modernization in the past few decades, and has expanded its diplomatic influence and presence in various regions and issues. Some argue that China’s ultimate goal is to dominate the world in economy, military, and diplomacy, and to replace the US as the global superpower. Others contend that China’s ambitions are more limited and pragmatic and that it seeks to protect its national interests and secure its development without provoking a major conflict with the US or other countries.
You Can Also Read: Can China be the Global Role Model for Peace?
There are several factors that could enable or constrain China’s potential dominance in the world. On the one hand, China has some advantages that could give it an edge over the US and other competitors, such as its large population, market, and resources, its political stability and centralized decision-making, its long-term vision and strategic planning, and its cultural and civilizational appeal. On the other hand, China also faces some challenges and risks that could limit its power and influence, such as its aging and declining population, its environmental and social problems, its dependence on foreign trade and investment, its lack of allies and partners, its ideological and value differences with the West, and its territorial and maritime disputes with its neighbors. Therefore, China’s rise is not inevitable or unstoppable, and its future role and status in the world will depend on how it manages its opportunities and challenges, and how it interacts with other actors and forces in the international system.
Economic Growth of China
China’s rise in the world economy has been nothing short of meteoric. Since the late 1970s, the country has undergone a transformation from a centrally planned economy to a dynamic market-oriented one, and its GDP has grown at an average of nearly 10 percent annually since Beijing started its economic reforms in 1978. As a result, China is now the world’s second-largest economy, after the United States, and its economic influence is felt in every corner of the globe.
In 2023, China’s economy grew by 5.2% year-on-year, outpacing many other nations despite global challenges like the Ukraine war and inflation. Thriving sectors include electric vehicles (EVs) and domestic tourism. However, growth momentum slowed in Q4 2023, and the stock and property markets face challenges. Market confidence and attracting foreign investors are priorities for sustained growth.
1.79 million college graduates will enter China’s job market in 2024, and ensuring high and stable growth is crucial to absorbing this new labor force. Economic challenges risk pushing a significant portion of China’s middle class out of this category. The government aims to strengthen market bonds and boost public confidence. In 2020, China’s share of global GDP reached 14.5%, surpassing its 2010 figure of 9.2%. 124 Chinese companies make their places on the Fortune 500 list, surpassing the U.S. In 2023 alone, its GDP reached a staggering $18.3 trillion.
China’s export-led growth strategy has been further bolstered by the government’s active role. In 2023 alone, fixed-asset investment reached a staggering $8.7 trillion, with significant sums directed towards infrastructure and education. Additionally, the creation of designated Special Economic Zones attracted foreign investment, further igniting growth.

Its domestic market is a powerhouse, fueled by a rising middle class with increasing disposable income. Retail sales in 2023 reached $7.8 trillion, showcasing the buying power within its borders. Moreover, China is actively investing in new technologies like AI and renewable energy, aiming for global leadership. Its AI research output surpassed the US in 2020, highlighting its ambitions in this field.
Military Influence
An economic powerhouse and burgeoning military force, China presents a challenge to the current world order. With a massive budget of $293 billion in 2022 (SIPRI data), second only to the U.S., and a staggering 2.04 million active personnel (IISS data), the world’s largest, China’s military modernization is proceeding at a rapid pace. Cutting-edge technologies like the J-20 stealth fighter and multiple aircraft carriers highlight this advancement, narrowing the gap with established military powers.
President Xi said, “The pursuit of the Chinese dream will bring to the world opportunities rather than threats, peace rather than turmoil, and progress rather than backwardness.”

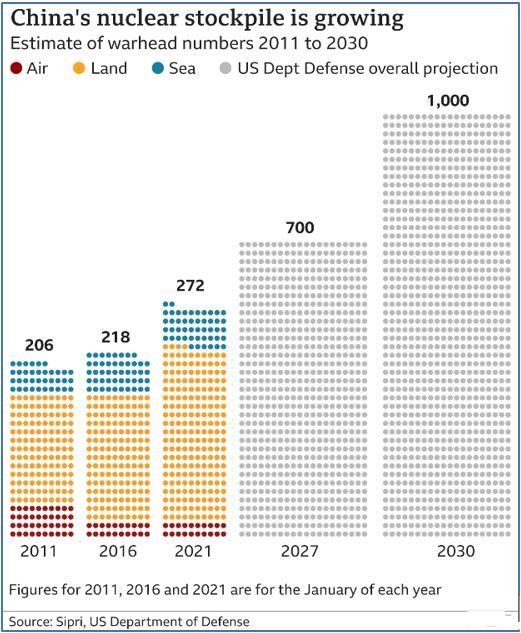
President Xi Jinping has outlined ambitious goals, aiming for a “world-class” military by 2035 and the ability to “fight and win wars” by 2049. This expansion, particularly in naval and nuclear forces, directly impacts the U.S. and its allies. The U.S. Navy estimates a nearly 40% increase in China’s naval capacity compared to theirs by 2040, both in quantity and quality of ships. Similarly, the U.S. Department of Defense projects a potential quadrupling of China’s nuclear arsenal by 2030, reaching at least 1,000 warheads.
Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence further add to China’s military ambitions. The Academy of Military Science aims to equip China with “intelligentised” warfare, leveraging disruptive technologies for future military applications. Reports suggest AI utilization in military robotics, missile guidance, and unmanned aerial and naval vessels.

China’s fast-growing economy and military strength are challenging the current world order. With big investments in new technology and ambitious plans from President Xi Jinping, China’s military is getting stronger, getting closer to big powers like the United States. This growth, especially in the navy and nuclear weapons, is changing the balance of power.
‘Wolf Warrior’Diplomacy
In the late 90s, China began to expand its diplomatic influence. China has experienced a significant change in its international diplomacy in the past decade, with the rise of a more aggressive and defiant style called “wolf warrior” diplomacy. This term is derived from the popular Chinese action movie series “Wolf Warrior,” where Chinese special forces fight against foreign enemies.
The use of wolf warrior diplomacy has triggered a growing discussion among academics and policymakers about its reasons and its effects on China’s global image and soft power. As China plays a more important role in world affairs, it is crucial to understand the motivations behind its diplomatic behavior and the outcomes of this assertive stance for managing the challenges of international relations in the 21st century.
One example of China’s peaceful and low-profile diplomacy is China’s joining the WTO. In 2001, China became a member of the WTO, indicating its willingness to be part of the global economic system and follow international trade rules. This event illustrates China’s peaceful diplomacy, as it aimed to collaborate with other countries and contribute to the global economy. Another example is China’s friendly-neighbor policy. China followed a “friendly-neighbor policy” in its dealings with neighboring countries in Asia, stressing peaceful coexistence, mutual respect, and economic cooperation.
Examples include the creation of the China-ASEAN Free Trade Area and the advancement of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) as a regional security mechanism. China’s role in multilateral diplomacy: China’s peaceful diplomacy was also shown in its active involvement in multilateral organizations and initiatives, such as the United Nations, the G20, and the Six-Party Talks on North Korea’s nuclear issue.
By participating in multilateral diplomacy, China sought to show its dedication to global governance and solving common problems. A core principle of Chinese diplomacy is the settlement of disputes through dialogue, and this method was a key element in fostering peace in various regions.
In March of 2023, a remarkable piece of news astonished the world. Mediated by China, Iran, and Saudi Arabia agreed to resume diplomatic relations and reopen their embassies. China’s efforts were widely praised by the international community as a triumph for peace and dialogue.
In conclusion, China’s path toward potential dominance in the global arena remains a topic of intense scrutiny and debate. Its economic prowess, military modernization, and assertive diplomacy have positioned it as a formidable player on the world stage. However, challenges such as demographic shifts, environmental concerns, and geopolitical tensions present significant hurdles to its ambitions. The evolution of China’s role in the international system will be shaped by its ability to navigate these complexities, engage in constructive dialogue with other nations, and uphold principles of mutual respect and cooperation. Whether China emerges as a dominant force or collaborates within a multipolar framework, its actions in the coming years will undoubtedly influence the course of global affairs.


