In the face of global economic challenges stemming from events such as the Ukraine-Russia war and the ongoing impact of the Covid-19 pandemic, Bangladesh has demonstrated resilience under the strategic leadership of the current government. Also, Bangladesh has achieved remarkable progress in reducing poverty, improving social indicators, and diversifying its exports. However, experts express concerns about the economy, citing pressure from declining reserves and escalating inflation.
You can also read: Can Bangladesh and Malaysia Formulate a Strategy to Coordinate Labor Migration?
To address these challenges, the government of Bangladesh is preparing the next annual budget for the fiscal year 2024-2025 as contractionary, aiming to reduce the inflation rate and restore financial stability, according to an official document.
GDP Target is Being Lowered
The contractionary budget implies that the government will spend less and possibly tax more, which will have a negative impact on economic growth. The official document reveals that the government has lowered its gross domestic product (GDP) growth target from 8.2% in the previous fiscal year to 6.9% in the next fiscal year. This is a significant downward revision, considering that Bangladesh has maintained an average GDP growth rate of 7.6% in the last five years.
Reasons for Lowering GDP Target
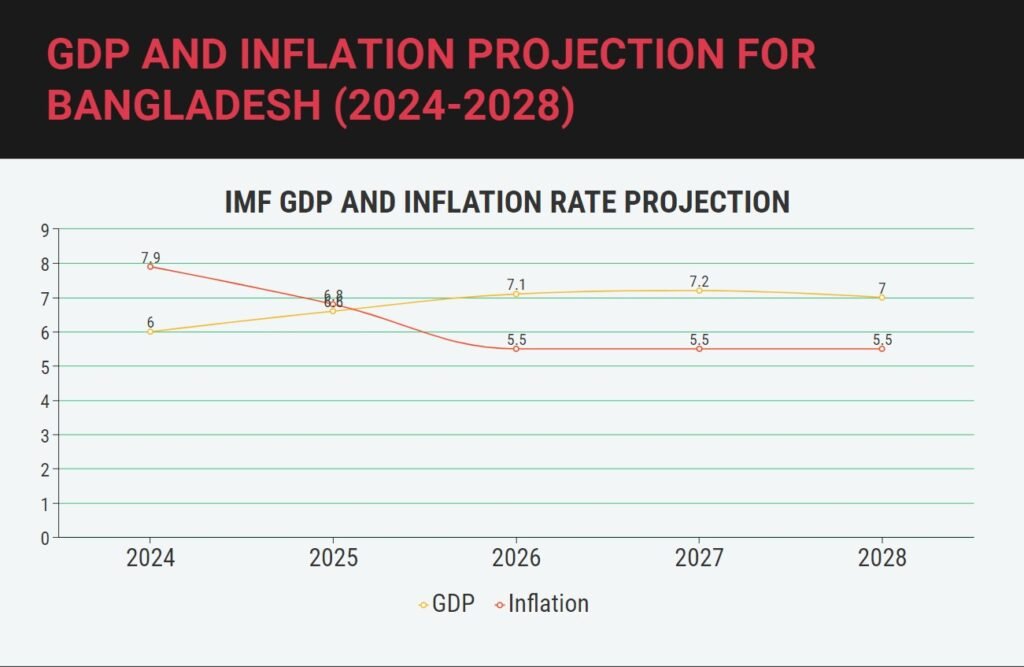
The main reason for lowering the GDP target is to curb the inflation rate, which has been hovering above 9% since 2023, well above the central bank’s target of 5.5%. High inflation erodes the purchasing power of consumers, especially the poor, and undermines the competitiveness of exports.
The initial inflationary pressure was triggered when the government increased spending to tackle the effects of the Covid-19 pandemic. The government increased its spending on health, social protection, and infrastructure, while the central bank lowered the interest rates and injected liquidity into the banking system.
However, the primary factor that drove recent high inflation is the external shock of the Russo-Ukrainian war. The sudden ‘shock rise’ in energy and food prices drove inflation to an all-time high while stressing the country’s foreign reserves.
Another reason for lowering the GDP target is to reduce the fiscal deficit and the public debt, which have reached unsustainable levels. The fiscal deficit, which measures the gap between the government’s revenue and expenditure, widened to 8.1% of GDP in the fiscal year 2023-2024, the highest in the country’s history.
The public debt, which measures the total amount of money that the government owes to domestic and foreign creditors, increased to 67.3% of GDP in the same period, the highest in South Asia. High fiscal deficit and public debt pose serious risks to economic stability, as they increase borrowing costs, crowd out private investment, and limit the fiscal space for future spending.
A Contractionary Budget
To address the inflationary and fiscal challenges, the government of Bangladesh is implementing a contractionary budget for the fiscal year 2024-2025. According to the official document, the government plans to reduce its total expenditure by 10.5% compared to the previous fiscal year and increase its total revenue by 8.7%.
The expenditure reduction will mainly affect non-development spending, such as subsidies, transfers, and wages, while the revenue increase will mainly come from tax reforms, such as broadening the tax base, simplifying the tax structure, and enhancing tax compliance. As a result, the government expects to narrow the fiscal deficit to 5.5% of GDP.
Why Is the Contractionary Budget Necessary?
The contractionary budget is necessary to restore the macroeconomic stability and confidence in the economy. By reducing government spending and increasing government revenue, the contractionary budget will reduce the aggregate demand and the money supply in the economy, which will ease the inflationary pressure and lower the interest rates. This will benefit the consumers, especially the low-income groups, who will see their real income and savings increase.
It will also benefit the exporters, who will see their products become more competitive in the international markets. Moreover, by reducing the fiscal deficit and the public debt, the contractionary budget will improve the fiscal sustainability and credibility of the government, which will attract more domestic and foreign investment and create more jobs and growth opportunities in the long run.
What Measures Will Be Implemented Under the Contractionary Policy?
The contractionary budget will be complemented by a contractionary monetary policy, which will be implemented by the central bank. The central bank will raise the policy rate, which is the interest rate at which it lends money to commercial banks, from 4.5% to 6.5% in the next fiscal year. This will reduce the availability and affordability of credit in the economy, which will further reduce the aggregate demand and the money supply.
The central bank will also use open market operations, which involve buying and selling government securities, to control the liquidity and the interest rates in the money market. The central bank will sell more government securities than it buys, which will reduce the money supply and increase the interest rates.
Why Is the Contractionary Budget Policy a Positive Measure?
The contractionary budget policy is a positive measure in the current economy, as it will help to achieve a more balanced and sustainable growth path. The contractionary policy will correct the macroeconomic imbalances that have accumulated in the economy due to the expansionary policies in the past.
It will also create more fiscal and monetary space for the government and the central bank to respond to future shocks and challenges. The contractionary policy will also support the structural transformation of the economy, which is essential for Bangladesh to graduate from the least developed country status and become a middle-income country.
The structural transformation involves diversifying the production and export base, upgrading the technology and skills, and improving the governance and institutions. The contractionary policy will facilitate the structural transformation by creating a more conducive environment for private sector development, innovation, and competitiveness.
What External Economic Challenges Might Bangladesh Face During the 2024-2025 Period?
Bangladesh might face several external economic challenges during the 2024-2025 period, such as the global economic slowdown, the trade tensions, and the climate change. The global economic slowdown, which is caused by the lingering effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, the Russo-Ukrainian war, and the Red Sea Crisis, might reduce the demand and the prices for Bangladesh’s exports, especially the readymade garments, which account for more than 80% of the total exports.
The trade tensions might disrupt the global supply chains and the market access for Bangladesh’s exports, as well as increase the volatility and risk in the global financial markets. Climate change, which is manifested by rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and environmental degradation, will affect agriculture, the infrastructure, and the livelihoods of millions of people in Bangladesh, especially in the coastal and low-lying areas.
How Will a Contractionary Budget Assist in Mitigating Possible Economic Challenges?
A contractionary budget will assist in mitigating external economic challenges by enhancing the resilience and adaptability of the economy. By reducing inflation and debt, the contractionary budget will improve the macroeconomic stability and the external balance, which will reduce the vulnerability of the economy to external shocks and fluctuations.
By creating more fiscal and monetary space, the contractionary budget will enable the government and the central bank to provide more stimulus and support to the affected sectors and groups, if needed.
By facilitating the structural transformation, the contractionary budget will help to diversify and upgrade the economy, which will increase the productivity and the competitiveness of the exports, as well as the capacity and the readiness of the economy to cope with the climate change.
Conclusion
Bangladesh’s contractionary budget for the fiscal year 2024-2025 is a necessary step for achieving economic stability and sustainability. The contractionary budget will reduce inflation and debt, which have been threatening economic performance and social welfare.
The contractionary budget will also create more fiscal and monetary space, which will allow the government and the central bank to respond to future shocks and challenges. The contractionary budget will also support the structural transformation, which will enable the economy to graduate from the least developed country status and become a middle-income country.
The contractionary budget, however, will also entail some short-term costs and trade-offs, such as lower growth, higher unemployment, and lower public spending. Therefore, the government should implement the contractionary budget with caution and care, and balance the need for fiscal consolidation with the need for social protection and inclusive development.


