The Bangladesh Delta Plan-2100 aims to secure a sustainable and resilient future, focusing on environmental, economic, and social development for the next century
Delta Governance Council, Bangladesh has been formed under the leadership of the Prime Minister to provide policy formulation, decision-making, strategic advice, and direction in the implementation of Bangladesh Delta Plan-2100. Delta Plan focuses on protecting vulnerable regions from climate impacts, emphasizing ecological restoration, biodiversity conservation, and sustainable agriculture. The plan also aims for socio-economic development by creating jobs and supporting local communities, resulting in environmental resilience, efficient water management, biodiversity conservation, and socio-economic progress for the regions involved.
You can also read: Tea Waves: Bangladesh Surpasses 2023 Records!
Recently, a gazette in this regard has been issued by the cabinet division. This council has 14 members. The Prime Minister has been made the Chairperson and the Planning Minister as the Vice-Chairman. Member Secretary is assigned to a member of the General Economics Division of the Planning Commission.
The Council’s scope of work includes policy formulation, decision-making, strategic advice, and direction in the implementation of Bangladesh Delta Plan-2100, to give directions for updating the Bangladesh Delta Plan and utilization of the Delta Fund.

However, on September 4, 2018, the National Economic Council (NEC) approved the Delta Plan, also known as “Delta Plan-2100.” This master plan includes long-term solutions for flood, river erosion, river management, waste management, urban and rural water supply, flood control, and drainage management.
BDP 2100: Delta Vision
The Bangladesh Delta Plan (BDP) 2100 is a comprehensive, long-term integrated plan aimed at addressing water resource challenges, climate change, and natural disasters in the Bangladesh Delta. Approved by the government on September 4, 2018, the plan encompasses various sector plans and policies, presenting a vision and strategies to ensure the delta’s safety by the end of the 21st century. The plan focuses on translating this vision into specific goals, including economic growth, poverty reduction, and targets for reducing vulnerability to water and climate-related hazards, as well as environmental conservation. The BDP 2100 serves as a roadmap for actionable interventions to secure the future of the region.
BDP 2100’s Strategy for Long-term Objectives
The BDP 2100 puts forth 3 overarching national objectives and 6 goals specific to the BDP 2100, all aimed at advancing the attainment of these broader aspirations.

Higher Level Goals:
- Eradicating severe poverty by 2030
- Attaining a status of upper-middle-income by 2030 and
- Establishing a thriving nation lasting beyond 2041
BDP 2100 Specific Goals:
- Safeguard communities against floods and climate change-induced disasters.
- Improve water security and optimize water usage efficiency.
- Foster sustainable and well-coordinated management of river systems and estuaries.
- Preserve wetlands and ecosystems while advocating for their responsible utilization.
- Establish robust institutions and ensure fair governance for effective water resources management within countries and across borders.
- Attain the optimal and harmonized utilization of both land and water resources.
Strategies of BDP 2100
3 different levels of strategies have been developed:
National Level:
- Flood Risk Management
- Fresh Wate
Hotspot Level:
- Coastal Zone (27,738 sq. km)
- Barind and Drought-Prone Areas (22,848 sq. km)
- Haor and Flash Flood Areas (16,574 sq. km)
- Chittagong Hill Tracts (13,295 sq. km)
- River Systems and Estuaries (35,204 sq. km)
- Urban Areas (19,823 sq. km)
Cross-cutting Themes:
- Sustainable Land Use and Spatial Planning
- Advancing Agriculture, Food Security, and Livelihood
- Trans-boundary Water Resources Collaboration
- Enhancing Dynamic Inland Water Transport
- Promoting Blue Economy Initiatives
- Integration of Renewable Energy Solutions
- Earthquake Preparedness and Resilience
BDP 2100 Investment Plan
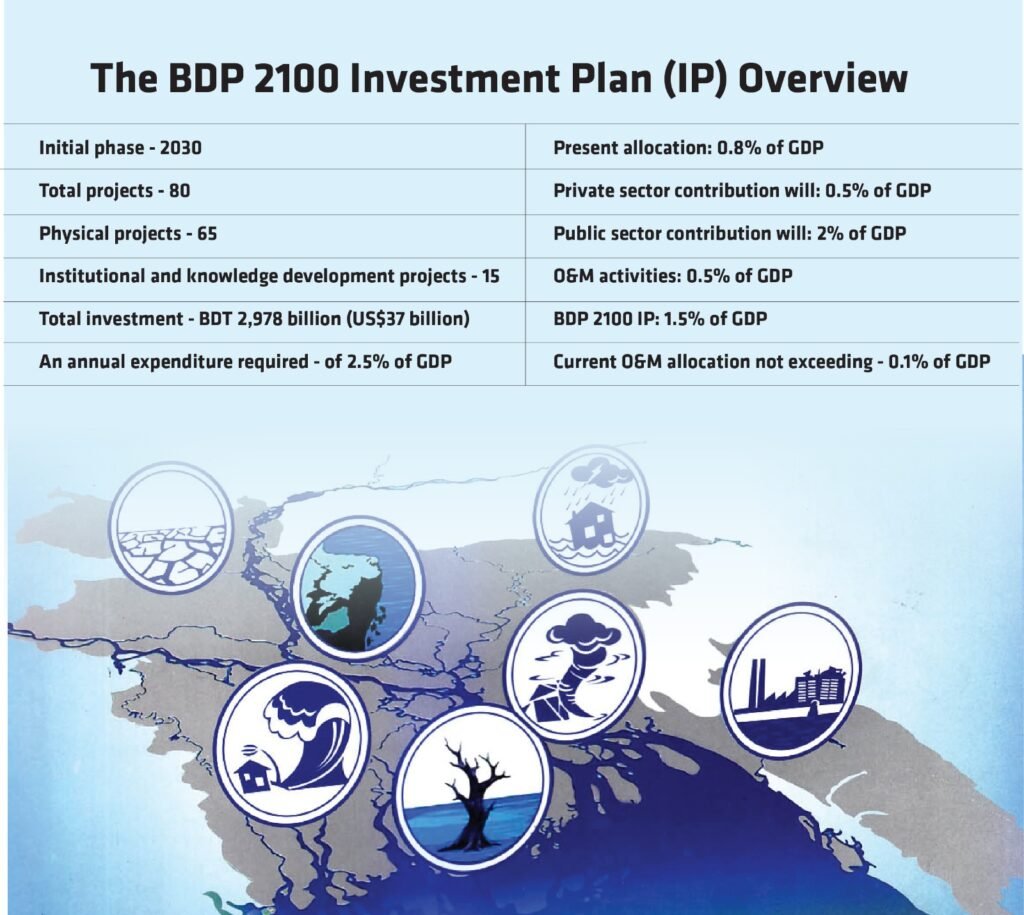
The BDP 2100 Investment Plan (IP) encompasses 80 projects, comprising 65 physical projects and 15 institutional and knowledge development projects during the initial phase until 2030. The overall capital investment required stands at BDT 2,978 billion (US$37 billion). These projects can commence within the next eight years, but due to the extensive scale and programmatic nature, certain constructions may span over decades.
To meet the investment needs for new projects and maintenance, an annual expenditure of about 2.5% of GDP is necessary. Presently, only 0.8% of GDP is allocated for this purpose. The private sector is expected to contribute 0.5% of GDP, while the public sector, accounting for 2% of GDP, will handle the majority. Of this, 0.5% of GDP is earmarked for O&M activities, with the remaining 1.5% falling under the BDP 2100 IP. It’s worth noting that the current O&M allocation is insufficient, likely not exceeding 0.1% of GDP.
In collaboration with the Government of the Netherlands, Bangladesh has initiated a 4-year project to support and oversee the implementation of BDP 2100. Several projects under the IP are already in progress, including the Dredging and Excavation of Canals and Small Rivers in 64 Districts, Dredging/Re-excavation of the Bangali-Karatoa-Fuljor-Hurasagor River System & Bank Protection Project, and the Urir Char Cross Dam in Noakhali. The World Bank has shown interest in financing BDP 2100 IP and is conducting a Feasibility Study for the Multi-Phase Jamuna Integrated River Basin Management, a component of the Integrated Jamuna-Padma Rivers Stabilization and Land Reclamation project.
Delta Collaboration MoU
In May 2012, the Government of Bangladesh and the Netherlands entered into a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for the development of the Bangladesh Delta Plan 2100, followed by another MoU on 16 June 2015 involving the World Bank to enhance water management in the Bangladesh Delta.
Investment Priorities
The foremost focus lies on investments in flood control, river erosion, and river management, including dredging, training, and navigability, constituting a primary chunk of approximately 35% of total Delta investments. Subsequently, urban water supply, sanitation, waste management, and drainage projects in major cities, given the escalating population and economic density, are expected to command a substantial share of around 25% of all delta investments. Lastly, addressing the evident lack of water and sanitation services in small towns and rural areas necessitates significant investments, potentially consuming up to 20% of the total BDP 2100 investment by FY2031 to achieve government targets for safe water supply and sanitation in these regions.
Delta Plan’s Outcomes
The outcomes of the Delta Plan are multifaceted, aiming to address various challenges and promote sustainable development. Primarily, the plan focuses on mitigating the impact of climate change and enhancing water resource management. By implementing adaptive measures, such as building resilient infrastructure and improving flood control systems, the Delta Plan aims to protect vulnerable regions from rising sea levels and extreme weather events.
Furthermore, the plan prioritizes ecological restoration and biodiversity conservation, fostering a healthier environment. It also emphasizes sustainable agriculture practices to ensure food security in the face of changing climate conditions. Additionally, the Delta Plan seeks to enhance socio-economic development by promoting job creation and supporting local communities.
The Delta Plan’s outcomes encompass environmental resilience, water management, biodiversity conservation, and socio-economic development, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient future for the regions it encompasses.
Conclusion
The establishment of the Delta Governance Council, led by the Prime Minister, marks a pivotal step in the implementation of the Bangladesh Delta Plan-2100. With a strategic vision outlined by Sheikh Hasina, the plan addresses complex challenges through a comprehensive approach, involving cross-cutting themes, investment priorities, and international collaboration. The BDP-2100 aims to secure a sustainable and resilient future, focusing on environmental, economic, and social development for the next century. The collaborative efforts and commitment to effective governance underscore Bangladesh’s dedication to mitigating climate change impacts and ensuring the well-being of its delta region.


