Key highlights:
- Bangladesh Bank’s policies align with the government’s economic goals and support a 6.5% GDP growth target while capping inflation at 7.5% for FY24
- The Standing Deposit Facility (SDF) rate is set to climb by 75 basis points, reaching 6.50% compared to the previous 5.75%
- The drop in CPI-based inflation from 9.41% in December 2023 to 8.75% 2024 in January is indicative of the positive outcomes resulting from monetary policy adjustments
- Despite the challenges posed by the pandemic, remittance inflows reached a record high of $24.8 billion in 2020 and increased by 21% year-on-year to $1.93 billion in November 2023
The Bangladesh Bank relies on the Monetary Policy Statement (MPS) as a crucial instrument to guide the economy in the right direction. While it used to be an annual occurrence, it is now issued biannually, showcasing the central bank’s adaptability to evolving economic conditions. Aligned with national growth and development goals, the Bangladesh Bank possesses a clear vision and strategy to achieve the desired outcomes of the MPS.
You can also read: Russia Proposes Exporting Wheat to Bangladesh, Explores Expanding Bilateral Trade
Despite formidable economic challenges, the released MPS acknowledges macroeconomic difficulties such as high inflation, low forex reserves, exchange rate fluctuations, and a balance of payments deficit. Bangladesh Bank’s policies align with the government’s economic goals and support a 6.5% GDP growth target while capping inflation at 7.5% for FY24.
The central bank has increased the policy rate by 25 basis points to 8%, stressing its commitment to combat inflation. While some economists may argue that this move is insufficient and tardy, it is crucial to recognize the delicate balance the Bangladesh Bank must strike between inflation and growth.
On the other hand, the Standing Deposit Facility (SDF) rate is set to climb by 75 basis points, reaching 6.50% compared to the previous 5.75%. This modification results in a contraction of the policy rate corridor, now ranging within ± 150 basis points instead of ± 200 basis points. In contrast, the Standing Lending Facility (SLF) rate is slated to decrease by 25 basis points, settling at 9.50% from its previous 9.75%.

Central Bank’s Move to Show Positive Results

Dealing with high inflation is a major focus for the government, yet there is a sense of optimism. The central bank’s proactive and flexible approach to tweaking monetary policy has proven effective in mitigating inflation. The drop in CPI-based inflation (consumer price index) from 9.41% in December 2023 to 8.75% 2024 in January is indicative of the positive outcomes resulting from these monetary policy adjustments.
Import costs are a channel through which the exchange rate influences inflation, which is acknowledged by the central bank. The Bangladesh Bank has exercised skillful control over the BDT/USD exchange rate, keeping it stable and warding off abrupt shocks. The BDT has undergone gradual and measured depreciation, in contrast to the rapid drops experienced by some other emerging economies.
As part of its recent monetary policy adjustments, the central bank lowered the private sector credit growth target from 11% to 10%. Additionally, the combined credit growth for both public and private sectors is expected to be 13.9% by the end of June 2024.
Contemplating the adoption of a ‘crawling peg system,’ the central bank aims to permit the exchange rate to respond to market dynamics within a limited range. This initiative is anticipated to bolster export competitiveness, alleviate pressure on reserves, and enhance the overall balance of payments.

Remittances, Investments, and Aid: Three Pillars of Foreign Exchange Strategy
The foreign exchange market operates dynamically. The fluctuation in the demand and supply of the US dollar is influenced by various factors such as trade, remittances, foreign direct investment, portfolio flows, and aid.
The Bangladesh Bank has been actively working to increase the supply of the US dollar by promoting remittances, attracting foreign investments, and securing external assistance. Despite the challenges posed by the pandemic, remittance inflows reached a record high of $24.8 billion in 2020 and increased by 21% year-on-year to $1.93 billion in November 2023. Additionally, foreign direct investment grew by 9.1% in the first half of the current fiscal year.
Multilateral agencies have also contributed to external assistance. These sources of foreign exchange have played a crucial role in mitigating the impact of the trade deficit and exchange rate depreciation.
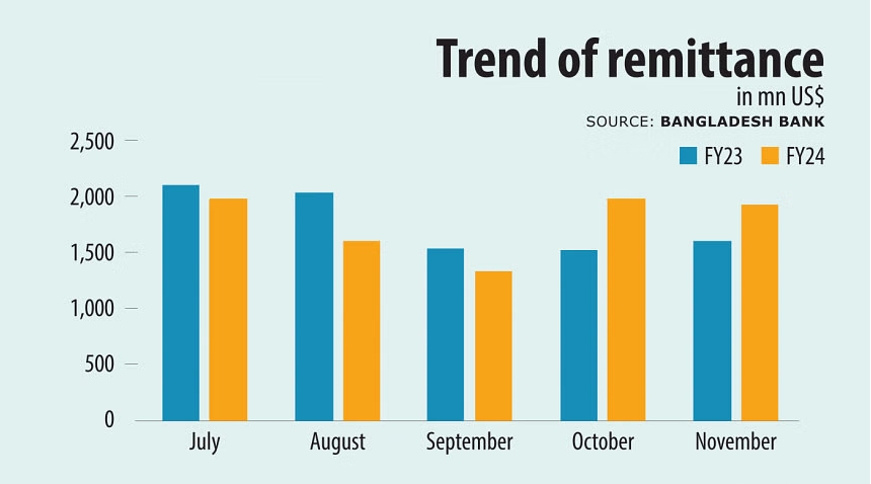
Why We Need Fiscal Discipline and Market Regulation?
Addressing inflation and exchange rate challenges is not solely the responsibility of the central bank; it is a collective effort involving the government and the private sector. The government must uphold fiscal discipline, rationalize subsidies, enhance public expenditure management, and implement structural reforms.
Simultaneously, the private sector must focus on improving productivity, efficiency, quality, and innovation. While the central bank cannot control the behavior of market players, it can monitor the market and intervene to prevent unfair practices and distortions.
Collaboration with relevant authorities is essential for effective market regulation and supervision.
The monetary policy statement is not a quick fix for economic issues but a practical document reflecting the current economic state and future prospects. It serves as a forward-looking and action-oriented guide for monetary policy decisions.
In conclusion, the success of the statement relies on cooperation and collaboration among stakeholders, including the government, private sector, civil society, and the general public. View the monetary policy statement not as a source of despair but as a positive signal for the future.


