Taking the lead, the five worst-performing currencies are the Lebanese pound, the Zimbabwean Dollar, the Syrian pound, the Argentine Peso, and the Turkish Lira
In the world of currency, the Kuwaiti dinar, a much sought-after option, and the US dollar, hailing from an influential economy, stand out as prime examples of strong currencies. A feeble economy frequently results in a devalued currency, yet a depreciated currency can often be attributed to its lack of demand. Factors like conflict, isolation, and rampant inflation often underlie the rapid depreciation of a currency.
You can also read: China’s Property Sector in Crisis: Debt Woes Affect Financial Sectors
The Federal Reserve’s expected increase in interest rates within the United States was foreseen as a factor likely to drive down the US dollar, which serves as the country’s official currency and enjoys widespread global use. The resurgence of USD has put pressure on the economic policies of prominent global players like China and Japan, compelling them to implement stimulus measures aimed at stabilizing their domestic currencies.
What determines the value of foreign currency?
Foreign exchange involves trading currencies in pairs, like purchasing US dollars with British pounds, and this gives rise to exchange rates, which indicate the relative value of one currency compared to another. Most currencies are categorized as ‘floating,’ implying that their value fluctuates based on supply and demand dynamics.
Leading financial stocks in the United States, such as Mastercard Incorporated (NYSE: MA), PayPal Holdings, Inc. (NASDAQ: PYPL), and JPMorgan Chase & Co. (NYSE: JPM), have all seen significant value increases due to the current economic conditions. According to the Commodity Futures Trading Commission, short positions on the dollar decreased to $7.17 billion in early September, down from $21.28 billion in late July, which marked a two-year high.
Which currencies are the top 15 underachievers in the market?
Data from foreign exchange company XE was used, starting with an initial dataset of the 50 currencies with the highest value against the US dollar on January 2, 2023. The percentage decrease was calculated by comparing these values to the currency’s worth against the US dollar on September 15, 2023. Digital coins were not included in this ranking.
Let’s take a look at the underperformers:
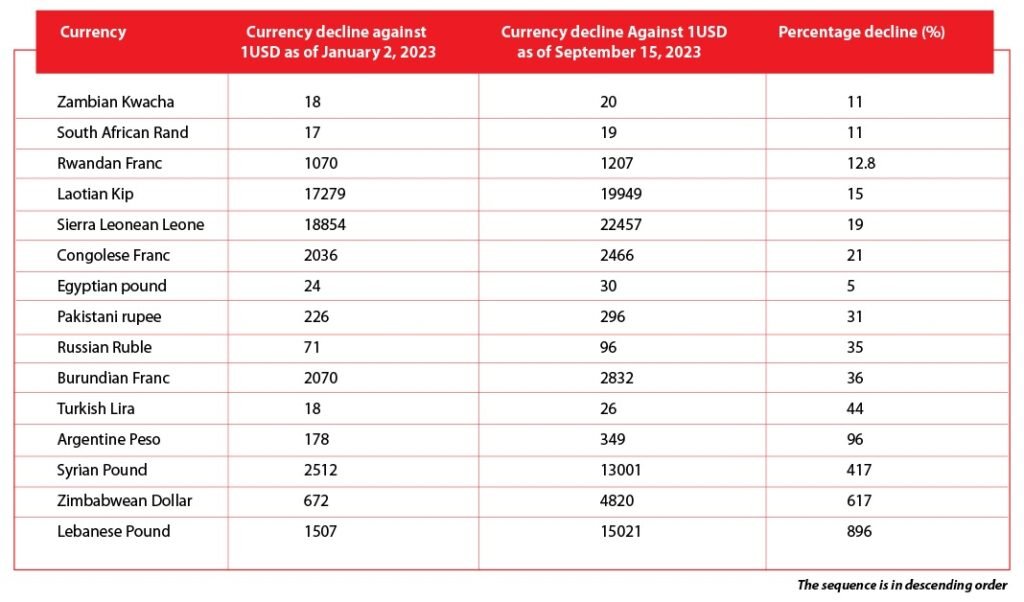
Overview of the Falling Currency Values
15. Kwacha is Zambia’s currency, and it replaced the British pound in 1964. However, it has faced recent challenges, due to factors such as reduced private sector spending, high inflation rates, and a central bank interest rate increase to 10% to combat inflation. Its currency is also uncertain due to debt restructuring and decreased copper production.
14. South African Rand is the official currency of South Africa. Interest rate hikes in the United States have negatively affected South Africa. China, Its largest trading partner, has had a significant influence. A slowdown in the Chinese economy has put pressure on the Rand, though recent stimulus measures from Beijing have provided some temporary relief.
13. Rwandan Franc is Rwanda’s official currency, located in Africa near Uganda. Persistent inflation has led the country’s central bank to raise interest rates, causing the currency to decline.
12. Lao Kip is the official currency of Laos, a Southeast Asian nation, since 1955. It has been losing value against the US dollar due to rising commodity prices, global financial conditions, and the influence of a slowing Chinese economy. Additionally, external liquidity issues, a growing circular debt, and substantial external debt repayments are contributing factors.
11. Sierra Leonean Leone is Sierra Leone’s official currency, located in West Africa near Guinea. Rising energy and food costs, partially attributed to the conflict in Ukraine, have led Sierra Leone to seek financial assistance from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
10. Congolese Franc is the official currency of the Democratic Republic of Congo. The Democratic Republic of Congo is considered one of the world’s poorest nations, with roughly two-thirds of its 100 million people living on less than $2.10 per day, according to the World Bank.
9. Egyptian Pound is Egypt’s official currency, and Egypt is a highly populated country in Africa. In recent months, urban inflation rates have surged, reaching 37.4% in August, up from 36.5% in the previous month. Macroeconomic challenges and a shortage of foreign currency, have led to a significant depreciation of the Egyptian Pound.
8. Pakistani Rupee is Pakistan’s official currency, used in the South Asian country adjacent to India and China. The government’s debt restructuring plan, including seeking assistance from the IMF, has attracted the attention of investors interested in Pakistan’s economy.
7. Russian Ruble is Russia’s official currency, which is the largest country with significant geopolitical influence globally. The Russian invasion of Ukraine led Western nations to impose strict sanctions on Russian imports, affecting key Russian exports like energy and food.
6. The Burundian Franc is Burundi’s official currency, a country in Africa bordering Rwanda. Economic challenges, such as growing government debt, ongoing inflation, and higher food prices, have caused the local currency to depreciate.
5. Turkish Lira is Turkey’s official currency. In August, Turkey’s annual inflation rate increased for the second consecutive month, reaching nearly 59%, exceeding market expectations of around 56%.
4. Argentine Peso is Argentina’s official currency. Despite the country’s recent FIFA World Cup win in 2022, its currency has experienced a significant decline due to various economic challenges. These challenges include a persistent current account deficit since 2018.
3. Syrian Pound is the official currency of war-torn Syria, which has been in internal conflict since 2011. Loss of oil-producing areas and economic troubles in neighboring Lebanon have caused the Syrian Pound to weaken.
2. The Zimbabwean Dollar is Zimbabwe’s official currency, situated in Africa between Zambia and South Africa. In contrast to other currencies globally, the Zimbabwean dollar has depreciated by an alarming 617% this year, prompting investors to seek the stability of the US dollar amid economic uncertainty.
1. The Lebanese Pound, Lebanon’s official currency, has faced severe devaluation due to the COVID-19 pandemic, a port explosion in 2020, and global events like the Russian invasion of Ukraine. These challenges compelled the central bank to print more money, resulting in hyperinflation and a significant rise in the value of the US dollar.
In conclusion, the value of foreign currencies is determined by a complex interplay of economic, geopolitical, and domestic factors. While strong currencies like the Kuwaiti dinar and the US dollar are characterized by robust economies and global demand, weaker currencies often suffer from various challenges. These challenges can include conflict, inflation, high debt, and decreased confidence in the currency.
The list of top 15 underachieving currencies in the market provides a snapshot of the struggles faced by these nations. From Zambia’s Kwacha to Lebanon’s Lebanese Pound, each currency’s decline can be attributed to a unique set of circumstances. These circumstances range from economic instability, inflation, and debt restructuring to the influence of global events and geopolitical conflicts.
It is evident that the value of a currency is a reflection of the economic health and stability of the issuing country. For investors and policymakers alike, understanding the factors behind currency depreciation is crucial for making informed decisions in the ever-changing world of foreign exchange.


